RAG vs. Agentic RAG
...explained visually

...explained visually


TODAY'S ISSUE
These are some issues with the traditional RAG system:
Due to this, Agentic RAG is becoming increasingly popular. Let's understand this today in more detail.
On a side note, we started a beginner-friendly crash course on RAGs recently with implementations: Read the first six parts here →
Think of agents as someone who can actively think through a task—planning, adapting, and iterating until they arrive at the best solution, rathar than just following a defined set of instructions. The powerful capabilities of LLMs make this possible.
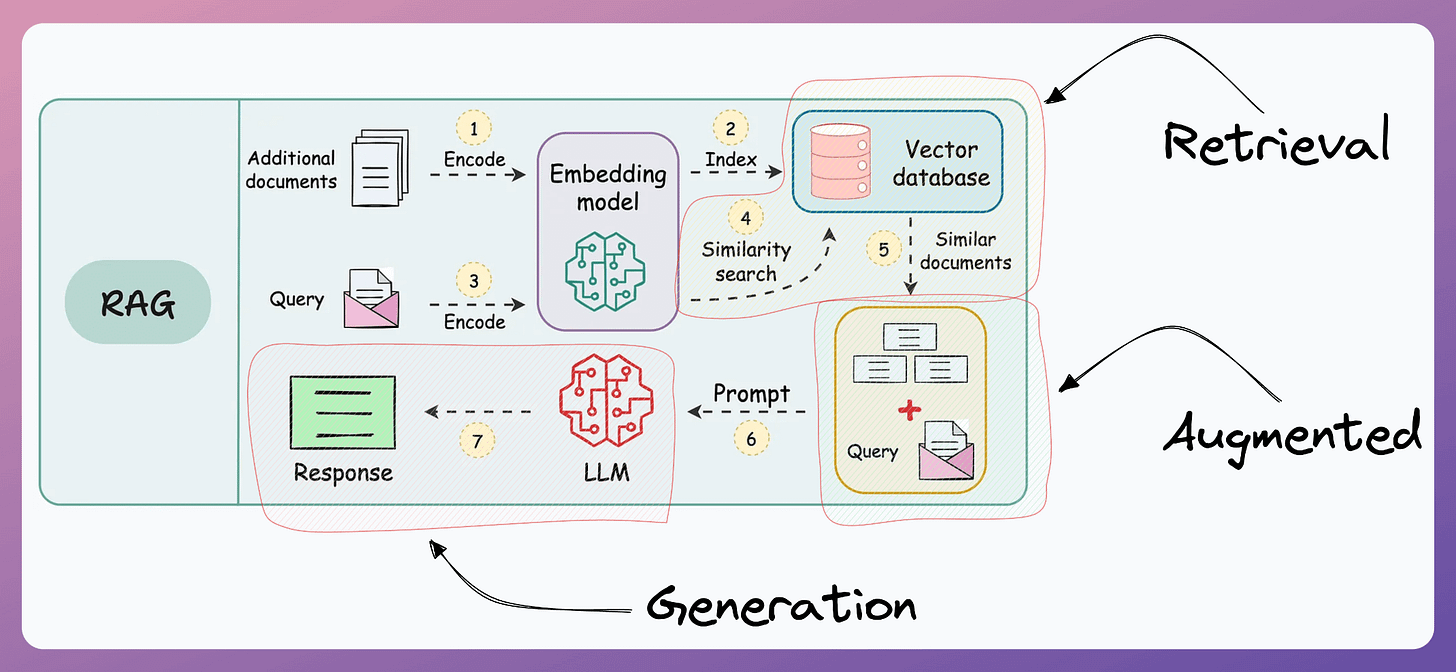
The workflow of agentic RAG is depicted below:
As shown above, the idea is to introduce agentic behaviors at each stage of RAG.
Let's understand this step-by-step:
Steps 1-2) The user inputs the query, and an agent rewrites it (removing spelling mistakes, simplifying it for embedding, etc.)
Step 3) Another agent decides whether it needs more details to answer the query.
Step 9) Either of the above two paths produces a response.
Step 10) A final agent checks if the answer is relevant to the query and context.
This makes the RAG much more robust since, at every step, agentic behavior ensures that individual outcomes are aligned with the final goal.
That said, it is also important to note that building RAG systems typically boils down to design preferences/choices.
The diagram above is one of many blueprints that an agentic RAG system may possess. You can adapt it according to your specific use case.
Going ahead, we shall cover RAG-focused agentic workflows in our ongoing RAG crash course in much more detail.
RAG is a key NLP system that got massive attention due to one of the key challenges it solved around LLMs.
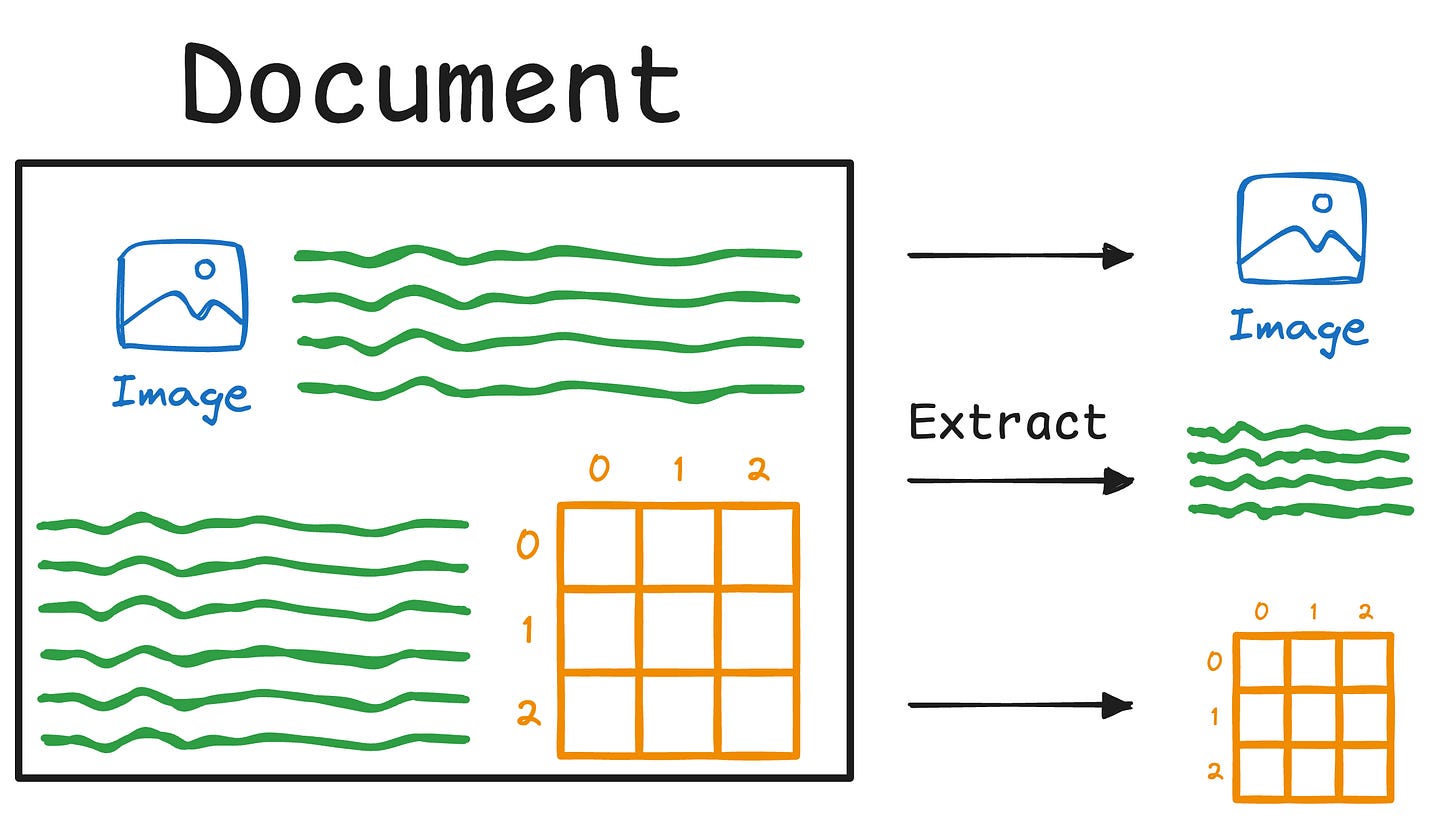
More specifically, if you know how to build a reliable RAG system, you can bypass the challenge and cost of fine-tuning LLMs.
That’s a considerable cost saving for enterprises.
And at the end of the day, all businesses care about impact. That’s it!
Thus, the objective of this crash course is to help you implement reliable RAG systems, understand the underlying challenges, and develop expertise in building RAG apps on LLMs, which every industry cares about now.
Of course, if you have never worked with LLMs, that’s okay. We cover everything in a practical and beginner-friendly way.
👉 Over to you: What does your system design look like for Agentic RAG?
Consider the model training loop in PyTorch shown below:
This means when the GPU is working, the CPU is idle, and when the CPU is working, the GPU is idle, as depicted below:
Ideally, you can transfer batch 2 when the GPU is training the model on batch 1.
Enabling this is quite simple in PyTorch.
First, define the DataLoader object with pin_memory=True and num_workers.
Next, during the data transfer step in the training loop, specify non_blocking=True:
Done!
Here's the speed comparison on MNIST:
Of course, this isn't the only technique to accelerate model training.
We covered 15 techniques (with implementation) to optimize M training here →