Build a Reasoning Model Like DeepSeek-R1
100% locally.

100% locally.


TODAY'S ISSUE
If you have used DeepSeek-R1 (or any other reasoning model), you must have seen that they autonomously allocate thinking time before producing a response.
Today, let’s learn how to embed reasoning capabilities into any LLM.
We'll train our own reasoning model like DeepSeek-R1 (code is provided later in the issue).
To do this, we'll use:
Let’s implement this.
We start by loading the Llama 3.1-8B model and the tokenizer using Unsloth.
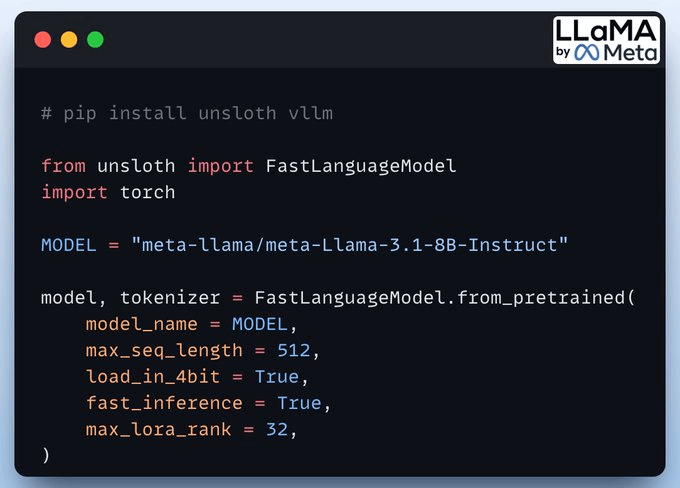
You can use any other open-weight LLM here.
We must use efficient techniques like LoRA to avoid fine-tuning the entire model weights.
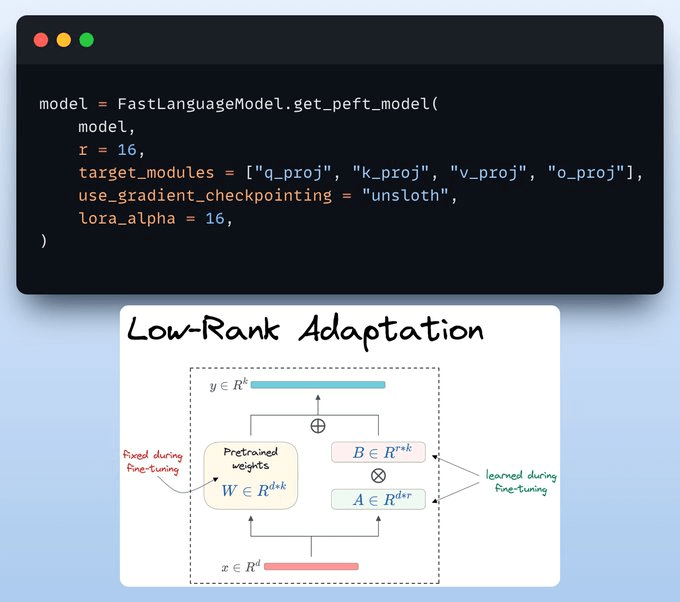
In this code, we use Unsloth's PEFT by specifying:
We load GSM8K (a math word problem dataset) and format prompts for reasoning.
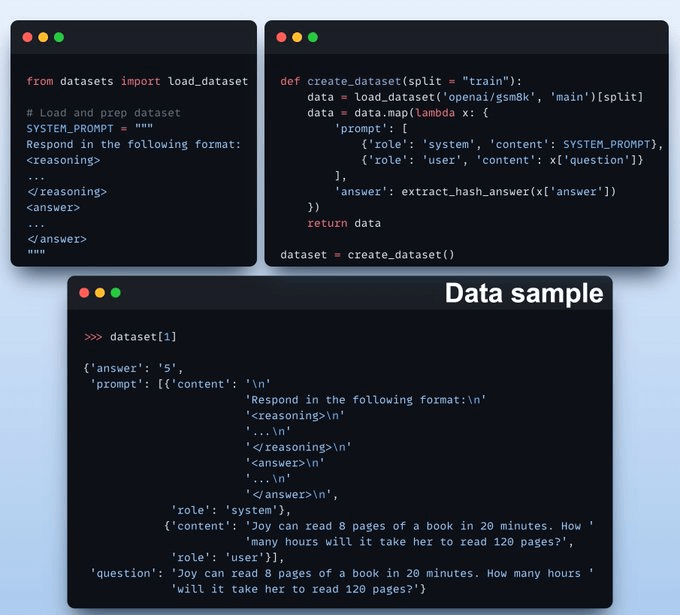
Each sample includes:
To guide fine-tuning, we define reward functions for:
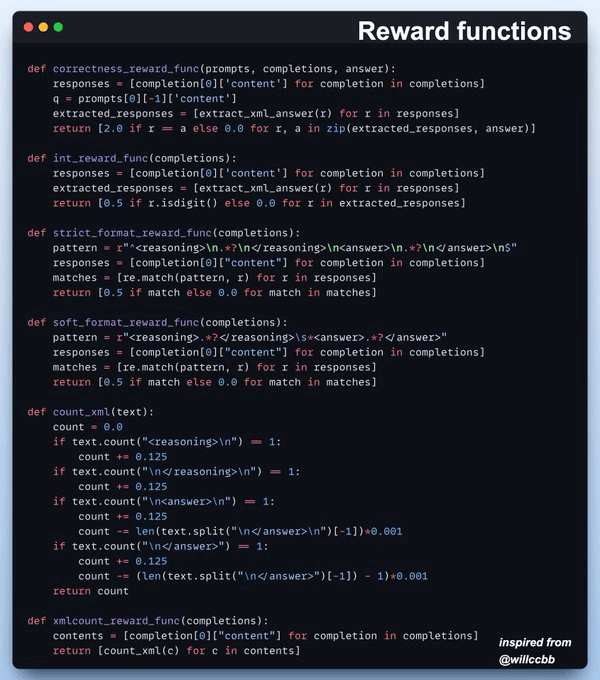
These help reinforce structured reasoning!
We employ GRPO, an RL method, to enhance reasoning. GRPO improves model performance without the need for a separate value function used in PPO.
If you don’t understand GRPO or PPO, don’t worry. We shall cover them soon. For now, just understand that these are reinforcement learning algorithms used to optimize decision-making policies (LLMs, in this case).
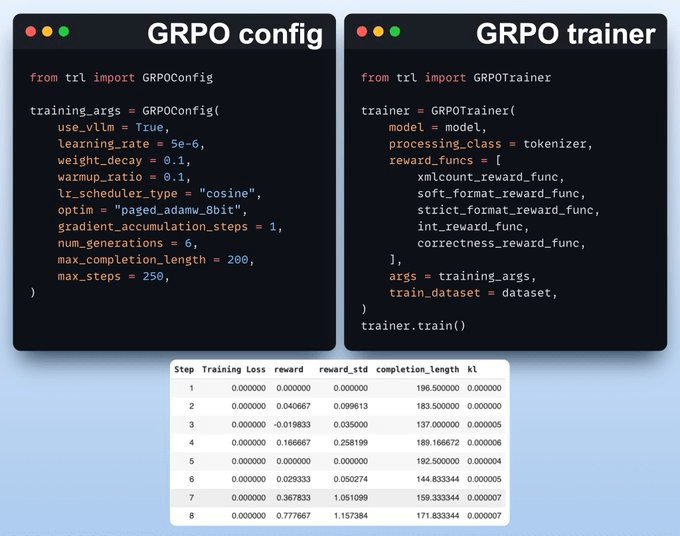
The setup includes:
Done!
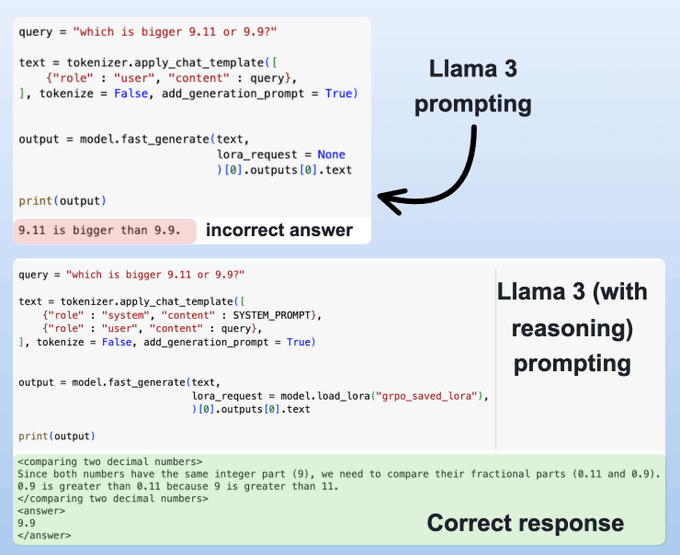
Before fine-tuning, Llama 3 struggles with numerical reasoning and provides incorrect answers.
After applying GRPO, the model not only gives the correct answer but also explains its reasoning.
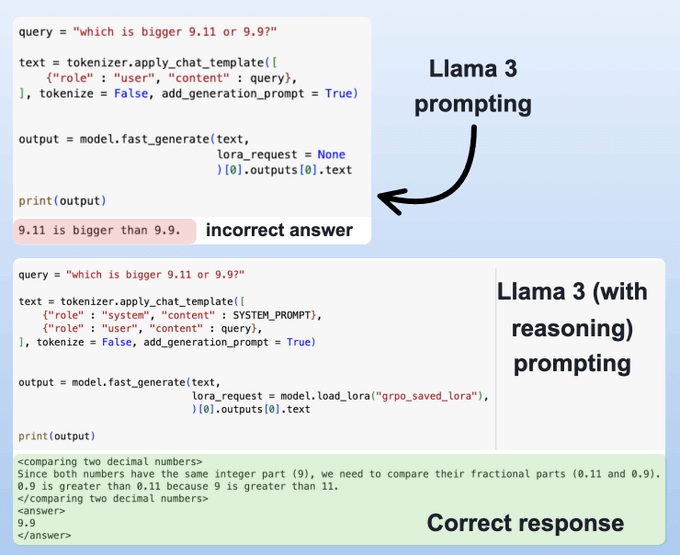
In this case, of course, it is a little flawed—”9 is greater than 11” when it may have wanted to say “90 is greater than 11” but you also need to consider that GRPO takes time, and I only ran the training script for 2 hours.
So this is expected and it will improve with subsequent training.
If you don’t know about LLM fine-tuning and want to learn, here’s some further reading:
You can find the code for today’s issue in our AI Engineering Hub repo here →
Thanks for reading!
Consider the size difference between BERT-large and GPT-3:
I have fine-tuned BERT-large several times on a single GPU using traditional fine-tuning:
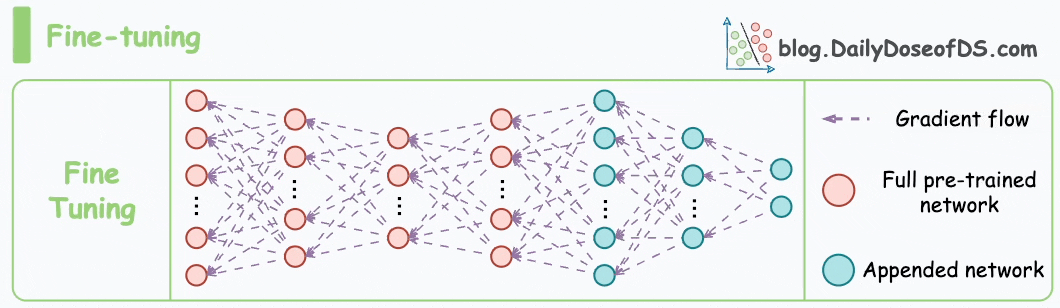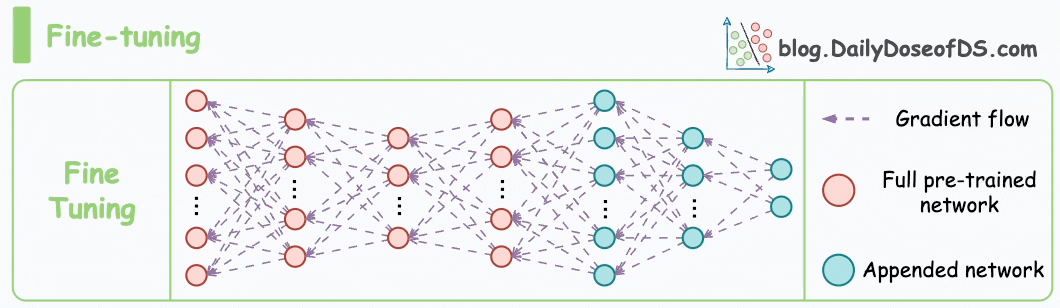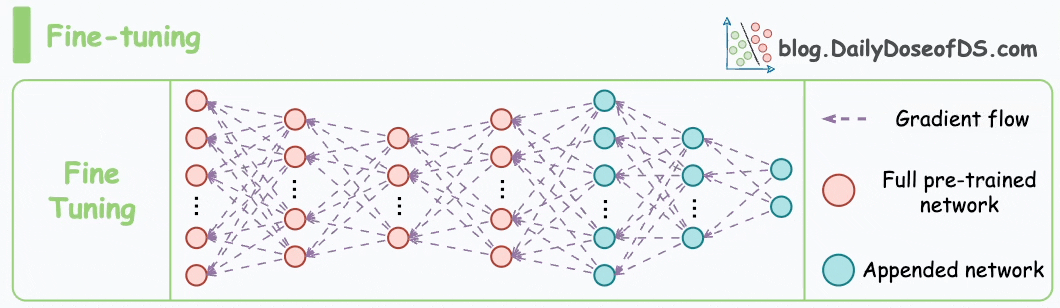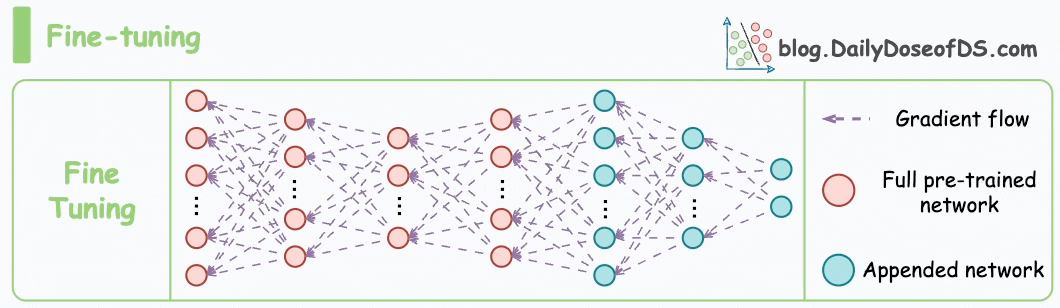
But this is impossible with GPT-3, which has 175B parameters. That's 350GB of memory just to store model weights under float16 precision.
This means that if OpenAI used traditional fine-tuning within its fine-tuning API, it would have to maintain one model copy per user:
And the problems don't end there:
LoRA (+ QLoRA and other variants) neatly solved this critical business problem.