5 Powerful MCP Servers
...to give superpowers to your AI Agents.

...to give superpowers to your AI Agents.


TODAY'S ISSUE
Integrating a tool/API with Agents demands:
To simplify this, platforms now offer MCP servers. Developers can plug them with Agents and use their APIs instantly. We also covered it in a recent newsletter issue (read here).
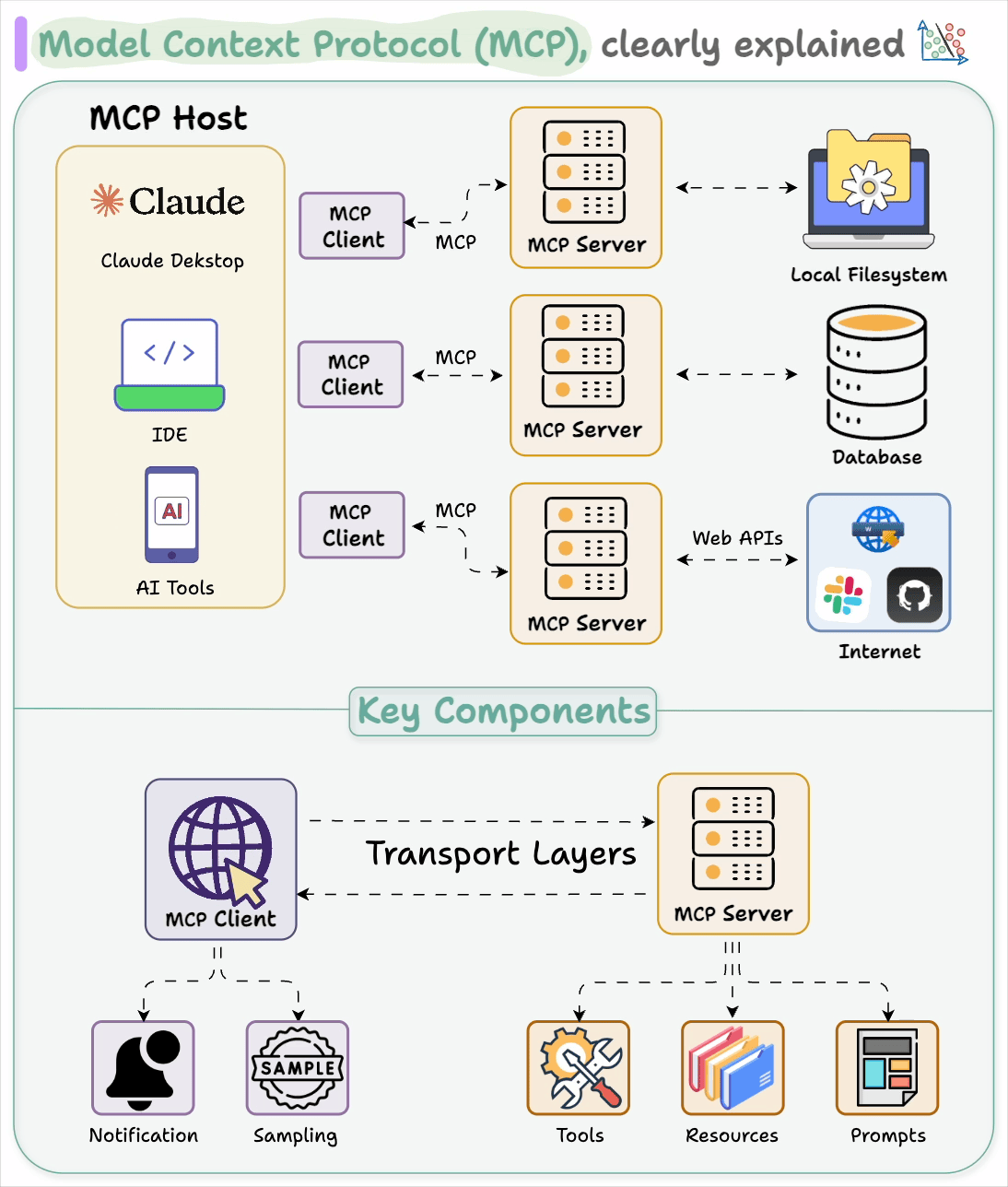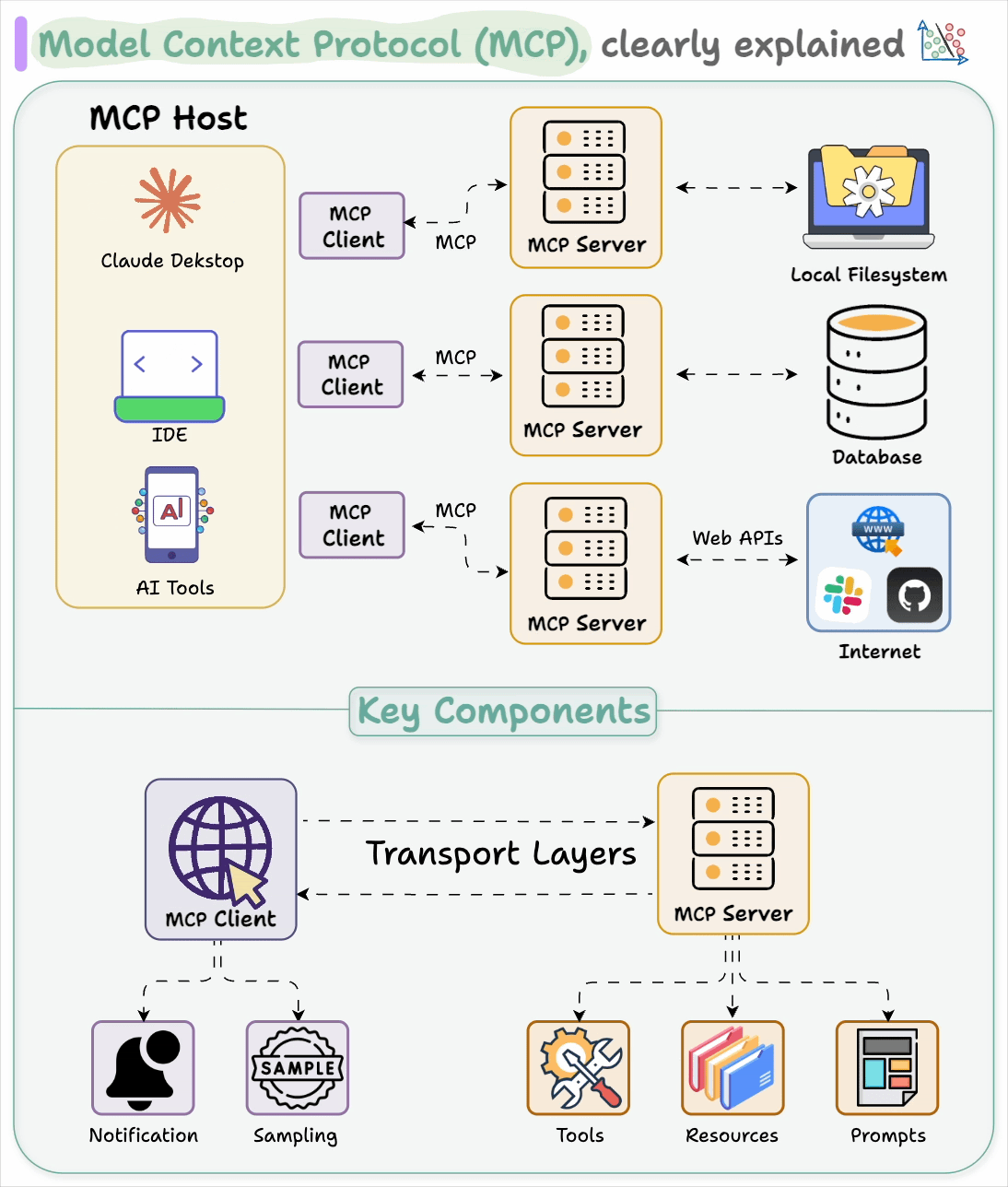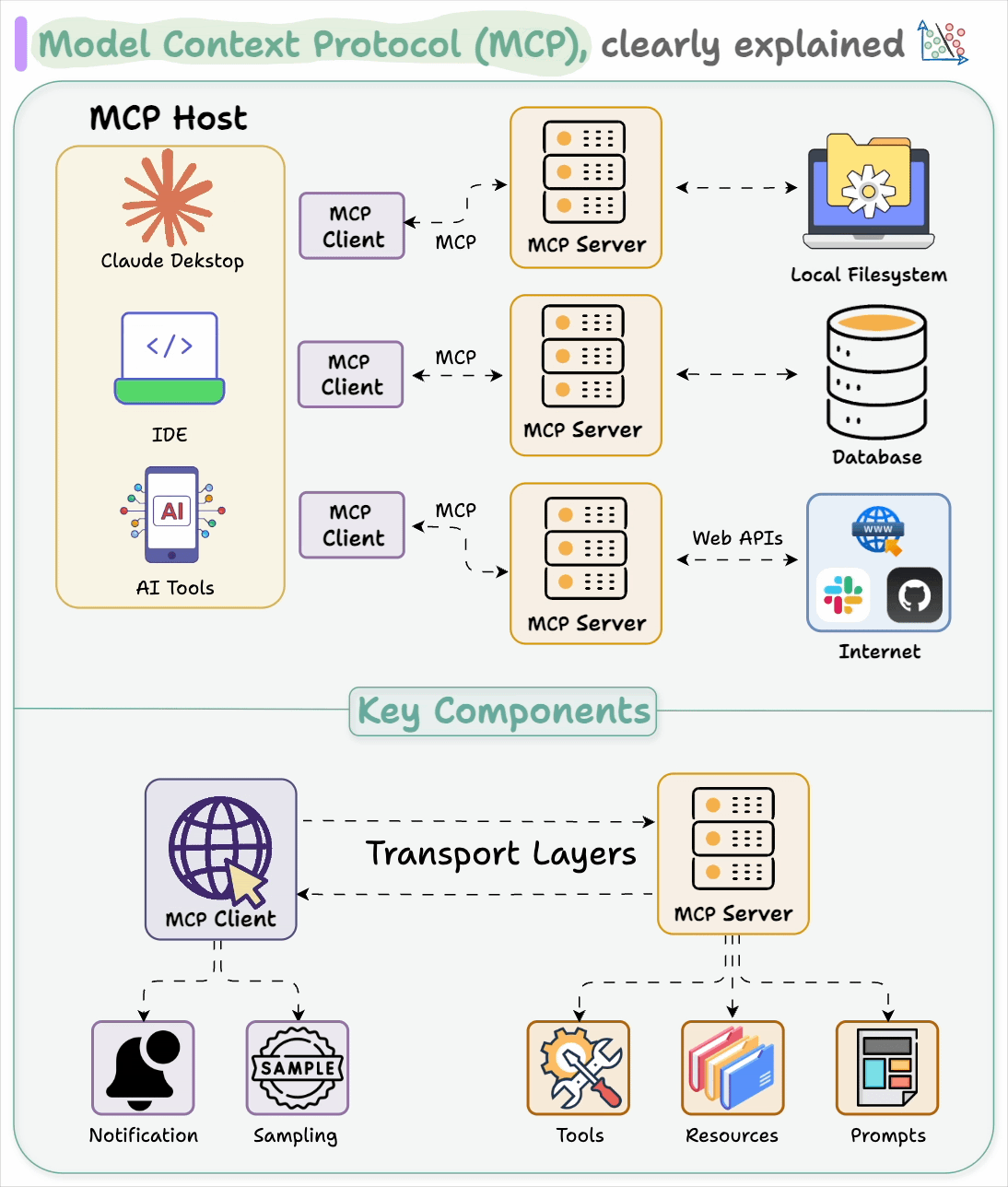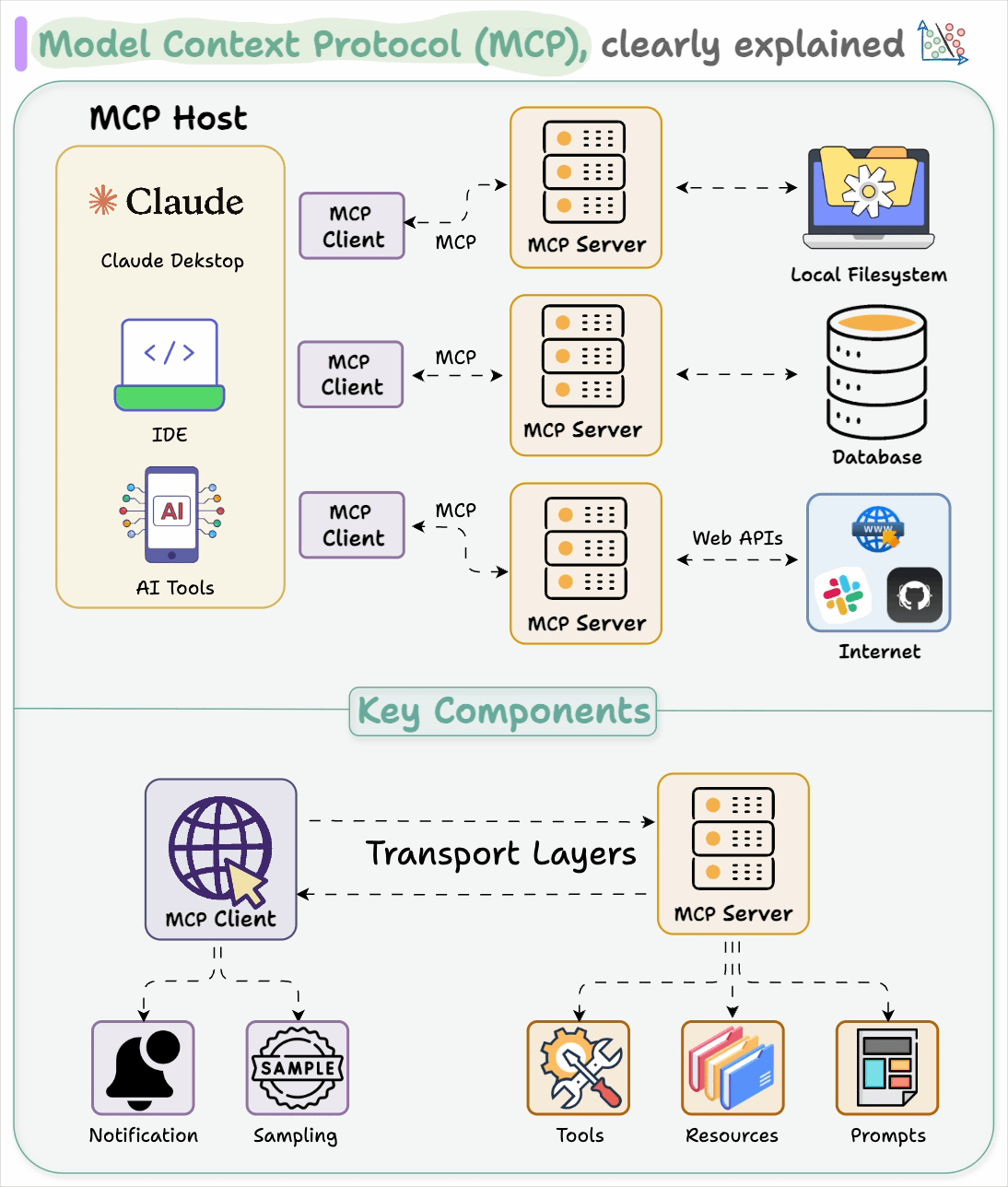
Below, let's look at 5 incredibly powerful MCP servers.
This adds powerful web scraping capabilities to Cursor, Claude, and any other LLM clients using Firecrawl.
Tools include:
Here’s a demo:
This allows Agents to initiate a browser session with Browserbase.
Tools include:
Here’s a demo:
This enables traceability into AI Agents and lets you monitor your LLM applications, by Comet.
Tools include:
Here’s a demo:
This enables Agents to use the Brave Search API for both web and local search capabilities.
Tools include:
This enables dynamic and reflective problem-solving through a structured thinking process.
Which ones are your favorite MCP servers? Let us know!
KV caching is a popular technique to speed up LLM inference.
To get some perspective, look at the inference speed difference from our demo:
The visual explains how it works:
On paper, implementing a RAG system seems simple—connect a vector database, process documents, embed the data, embed the query, query the vector database, and prompt the LLM.
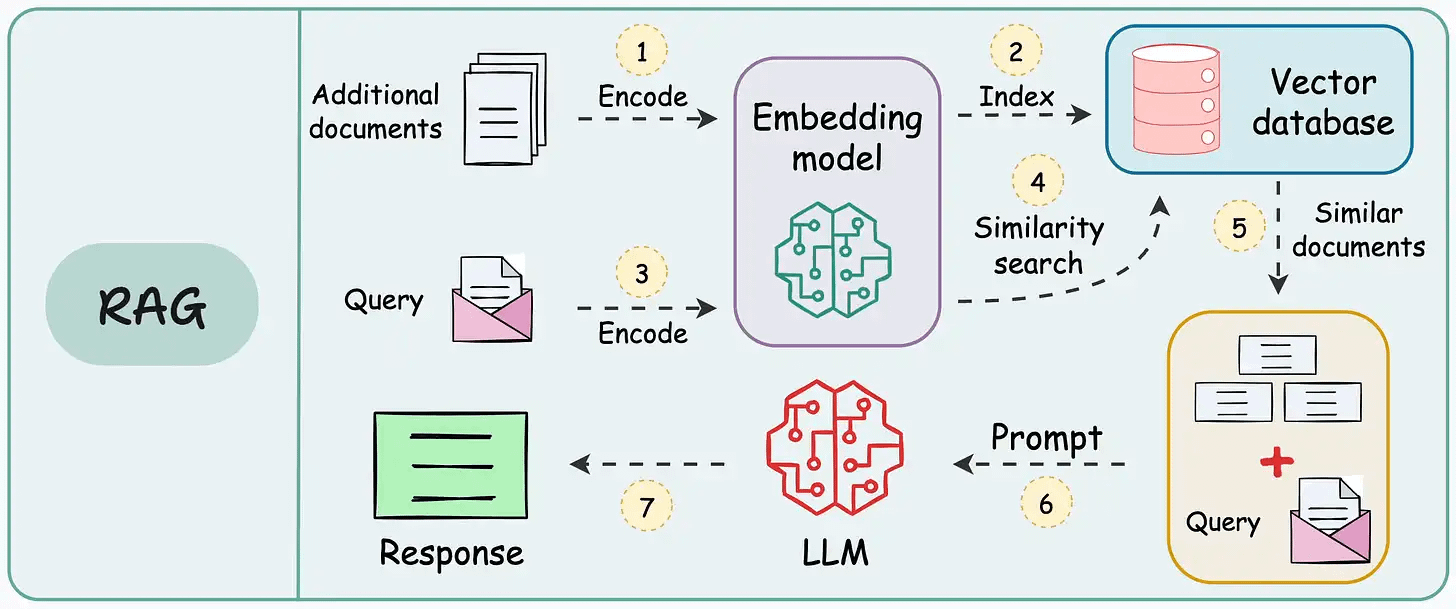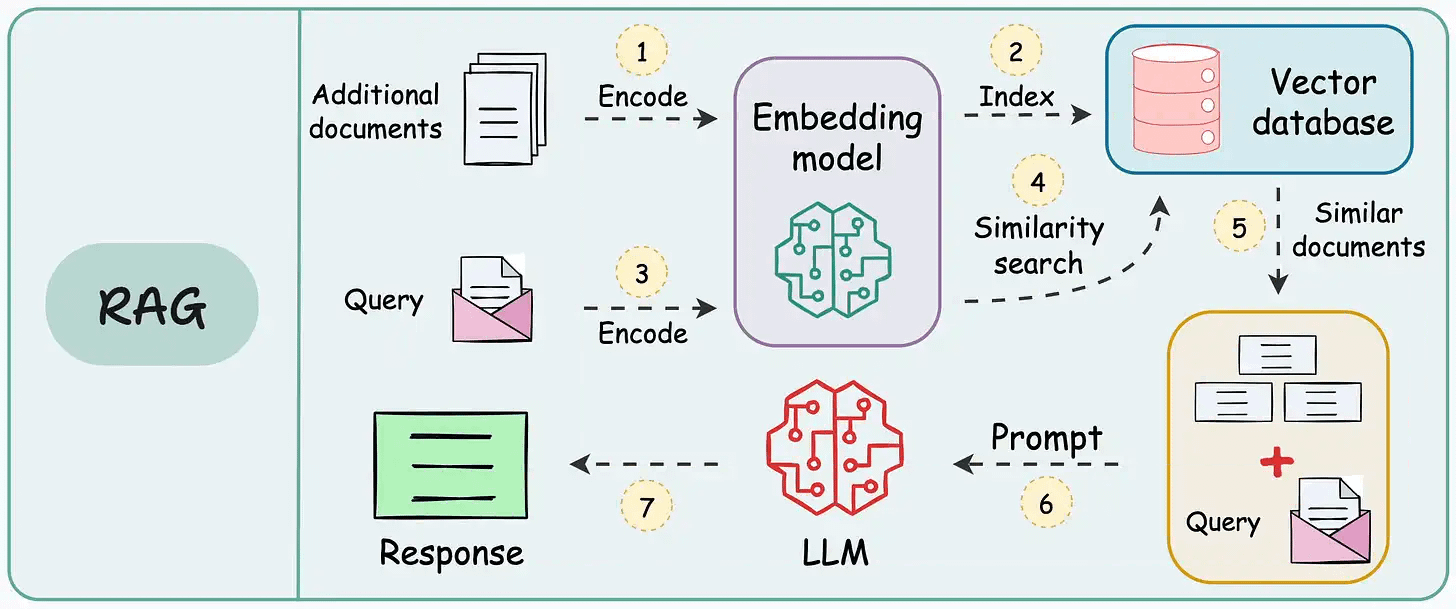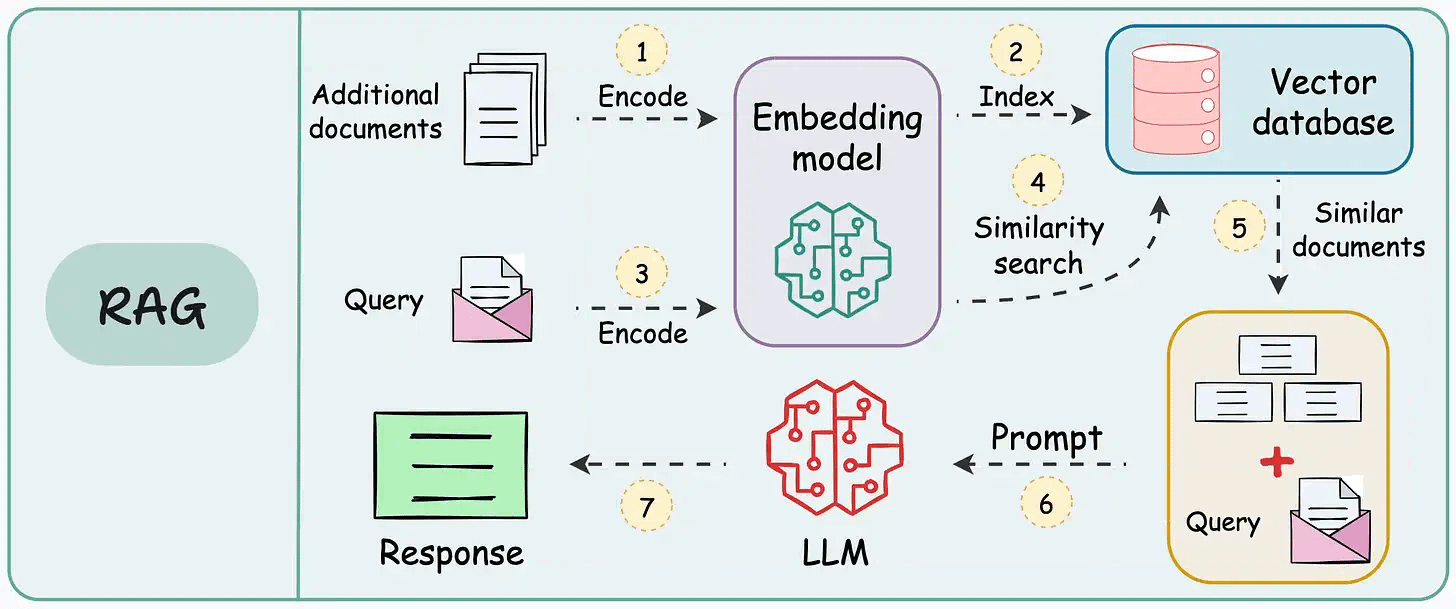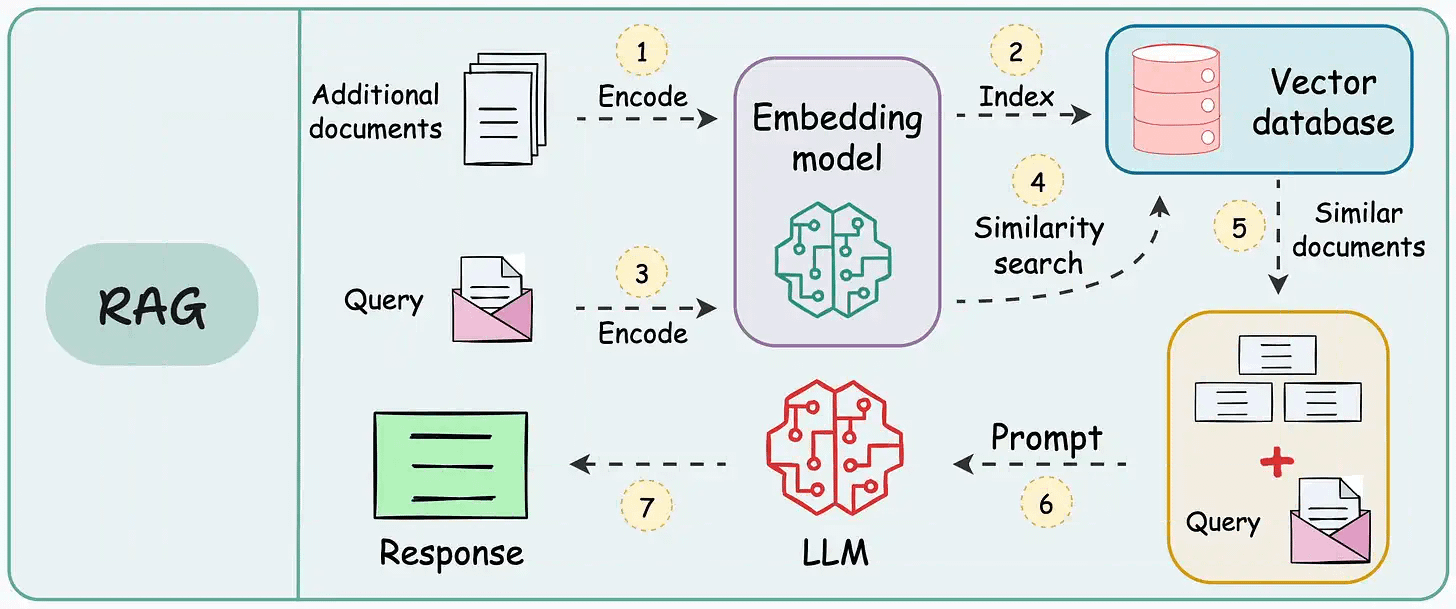
But in practice, turning a prototype into a high-performance application is an entirely different challenge.
We published a two-part guide that covers 16 practical techniques to build real-world RAG systems: