[Hands-on] RAG over audio files
...using AssemblyAI and DeepSeek-R1

...using AssemblyAI and DeepSeek-R1


TODAY'S ISSUE
While most RAG systems are built over text, plenty of data exists as speech (audio) and we need reliable ways to do RAG over them.
So today, let’s build a RAG app over audio files with DeepSeek-R1.
Here’s an overview of our app:
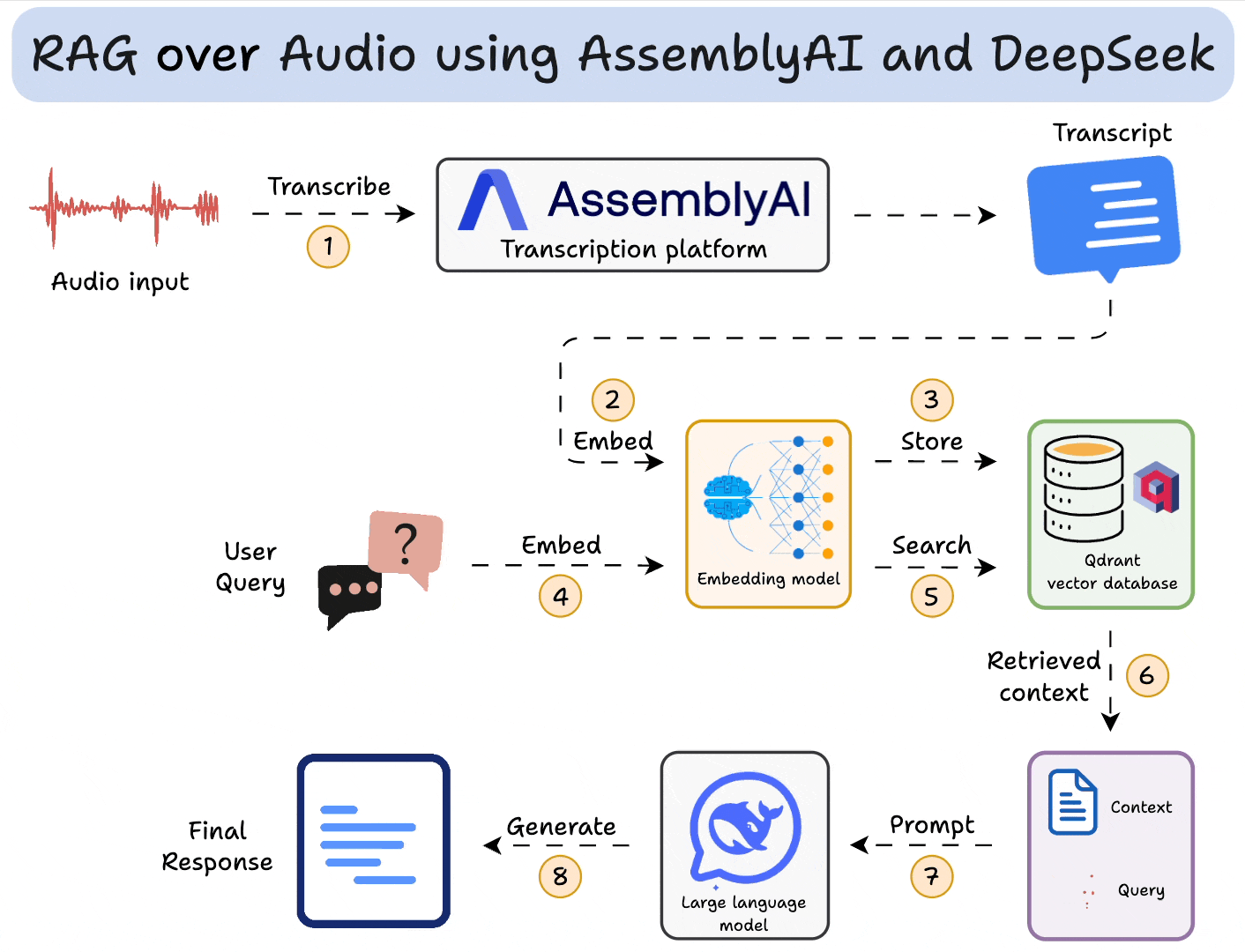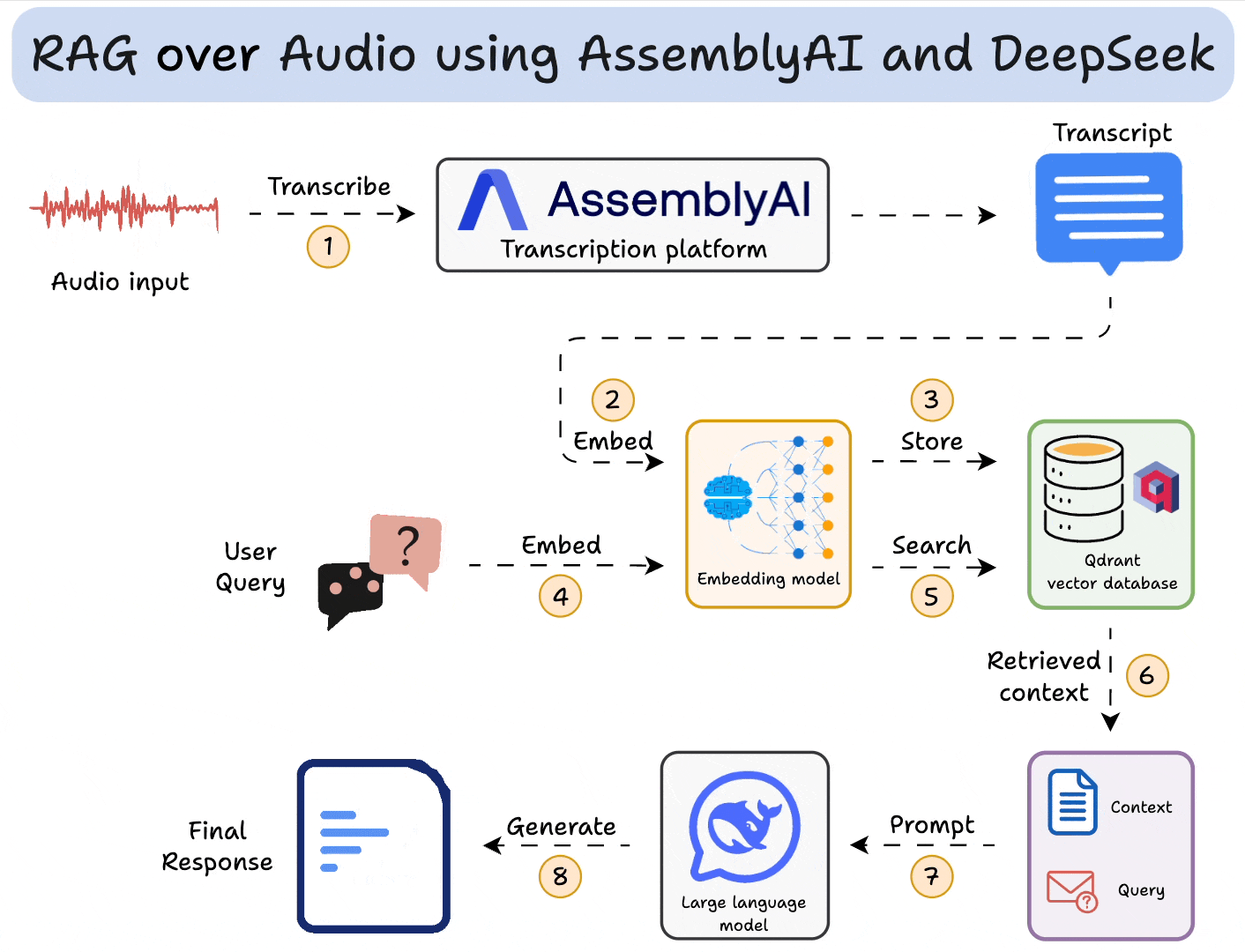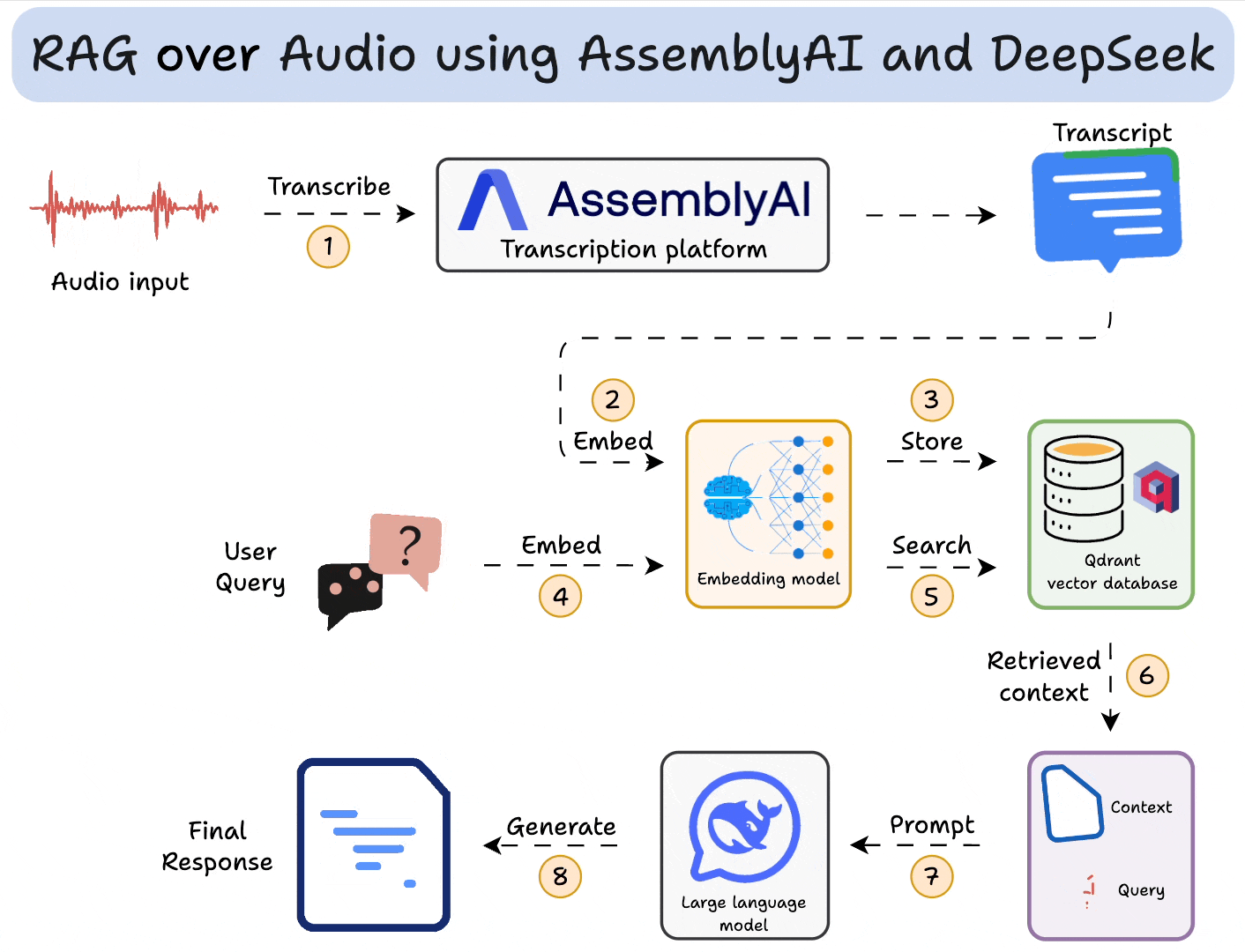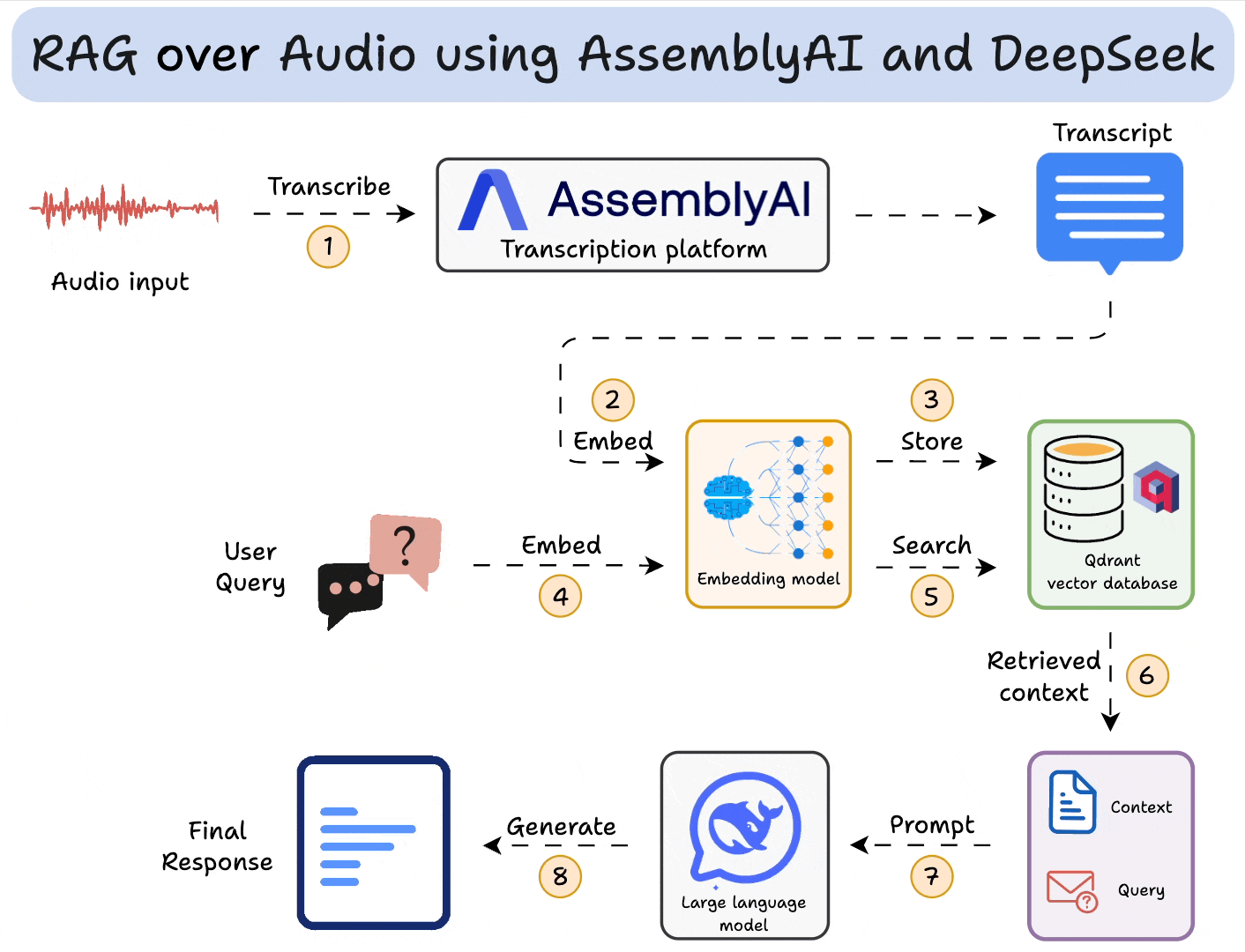

AssemblyAI has always been my go-to for building speech-driven AI applications.
It’s an AI transcription platform that provides state-of-the-art AI models for any task related to speech & audio understanding.
Now let's jump into code!
The GitHub repo is linked towards the end of this issue.
To transcribe audio files, get an API key from AssemblyAI and store it in the `.env` file. Get the API key here →

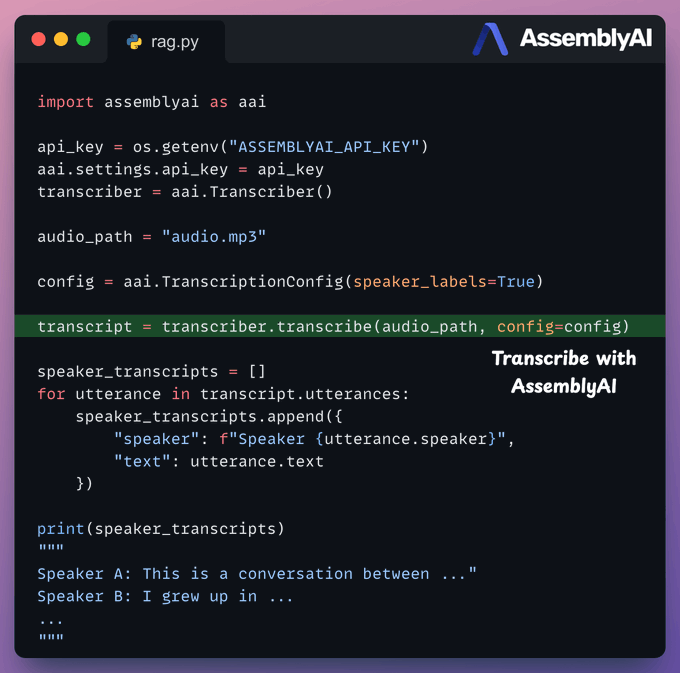
Next, we use AssemblyAI to transcribe audio with speaker labels. To do this:
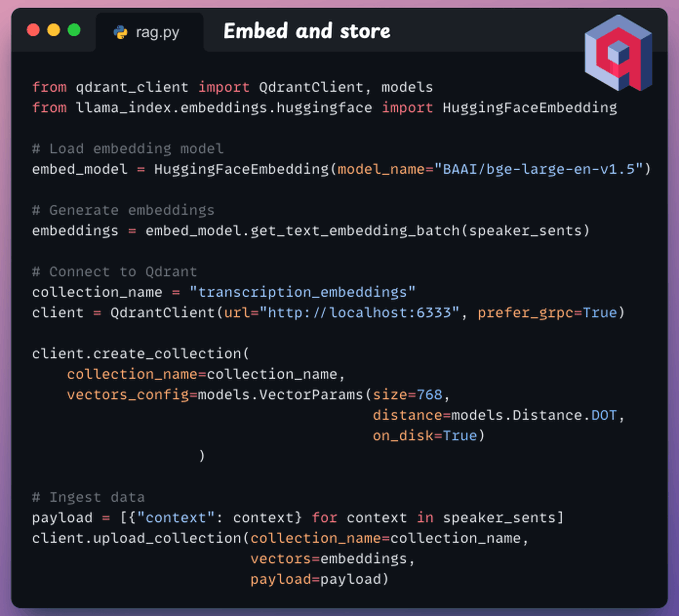
Moving on, we embed transcripts and store them in a vector database. To do this, we:
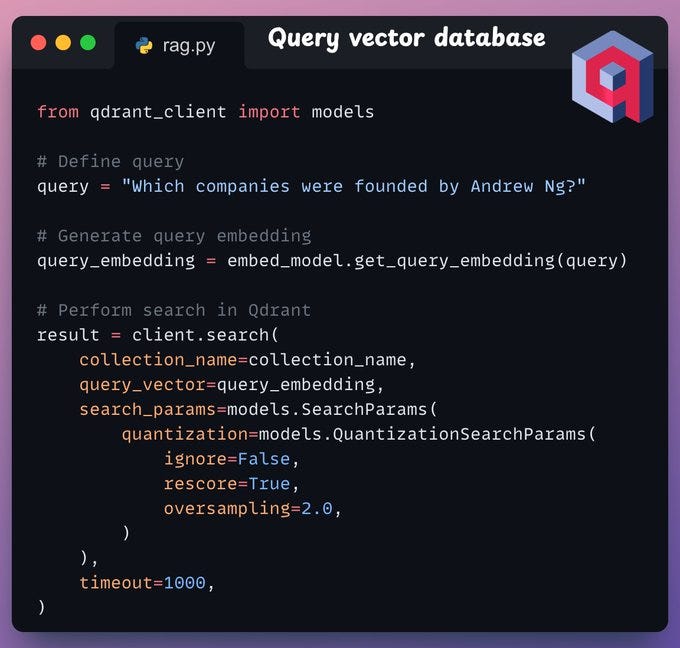
Now comes retrieval, where we query the vector database to retrieve sentences in the transcripts that are similar to the query:
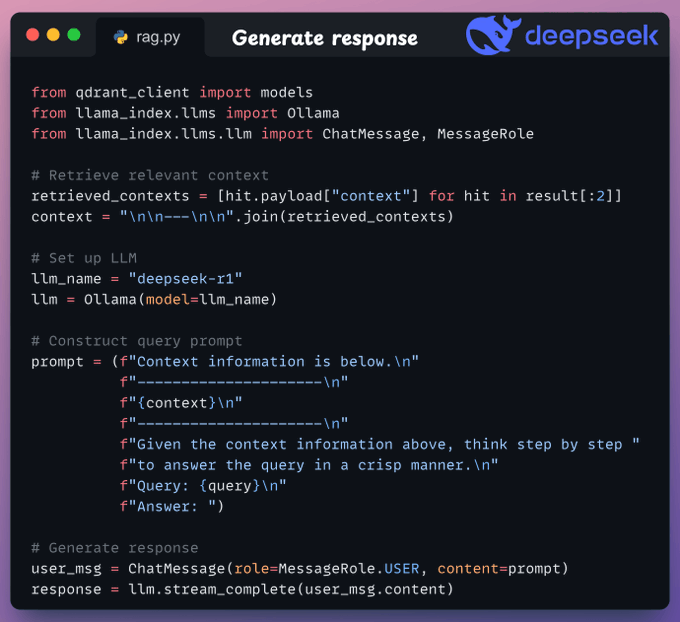
Finally, after retrieving the context:
To make this accessible, we wrap the entire app in a Streamlit interface. It’s a simple UI where you can upload and chat with the audio file directly:
That was simple, wasn’t it?
The code is available here: RAG over audio files.
We first used AssemblyAI over two years ago, and in my experience, it has the most developer-friendly and intuitive SDKs to integrate speech AI into applications.
AssemblyAI first trained Universal-1 on 12.5 million hours of audio, outperforming every other model in the industry (from Google, OpenAI, etc.) across 15+ languages.
Recently, they released Universal-2, their most advanced speech-to-text model yet.
Here’s how Universal-2 compares with Universal-1:
Its performance compared to other popular models in the industry is shown below:
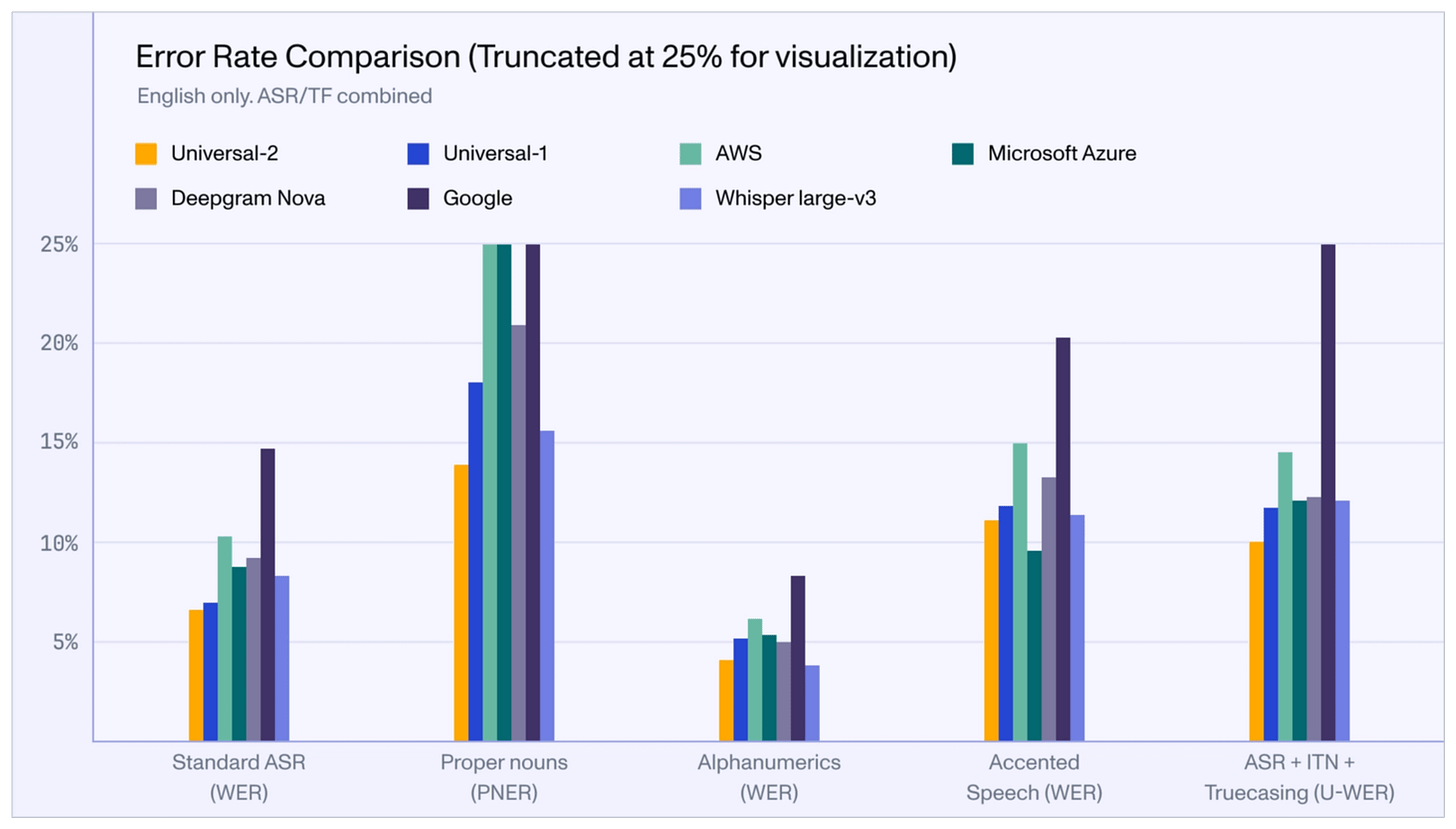
Isn’t that impressive?
We love AssemblyAI’s mission of supporting developers in building next-gen voice applications in the simplest and most effective way possible.
They have already made a big dent in speech technology, and we're eager to see how they continue from here.
Get started with:

Their API docs are available here if you want to explore their services: AssemblyAI API docs.
🙌 A big thanks to AssemblyAI, who very kindly partnered with us on this demo and allowed us to showcase their industry-leading AI transcription services.
👉 Over to you: What would you use AssemblyAI for?
Thanks for reading!