[Hands-on] Building a Real-Time AI Voice Bot
...AssemblyAI + OpenAI + ElevenLabs.

...AssemblyAI + OpenAI + ElevenLabs.


TODAY'S ISSUE
AssemblyAI has always been my go-to for building speech-driven AI applications.
It’s an AI transcription platform that provides state-of-the-art AI models for any task related to speech & audio understanding.
Today, let’s build the following real-time transcription apps with AssemblyAI.
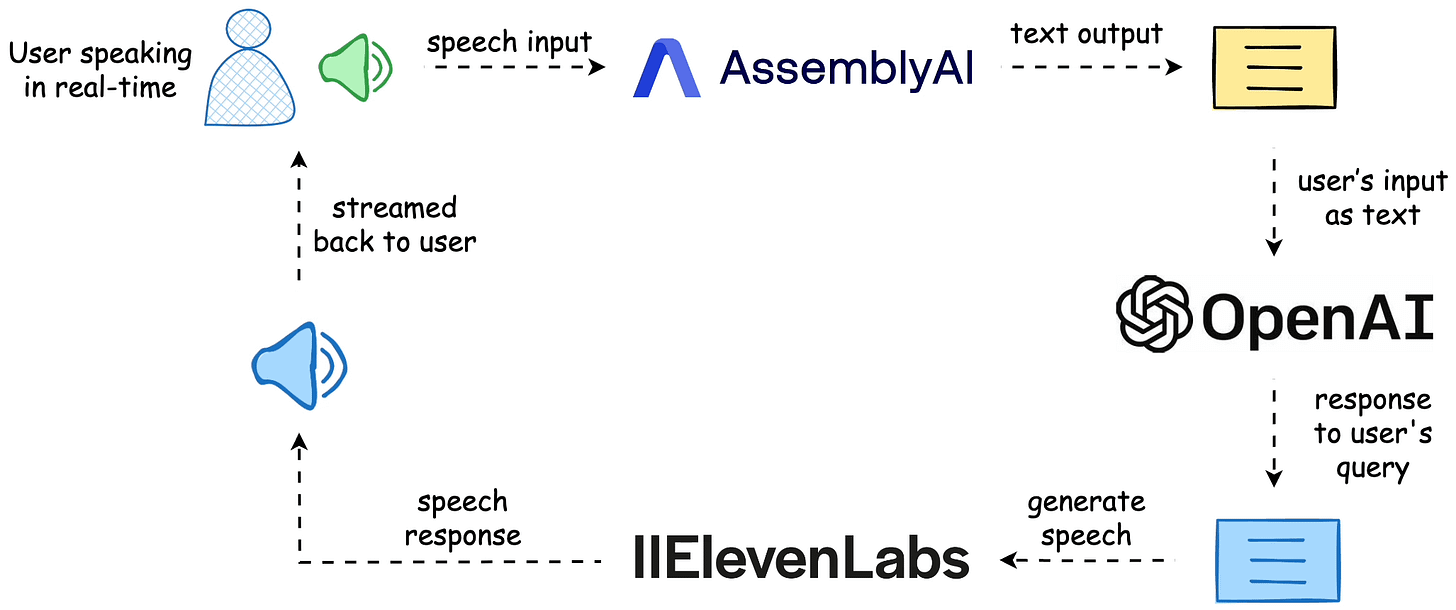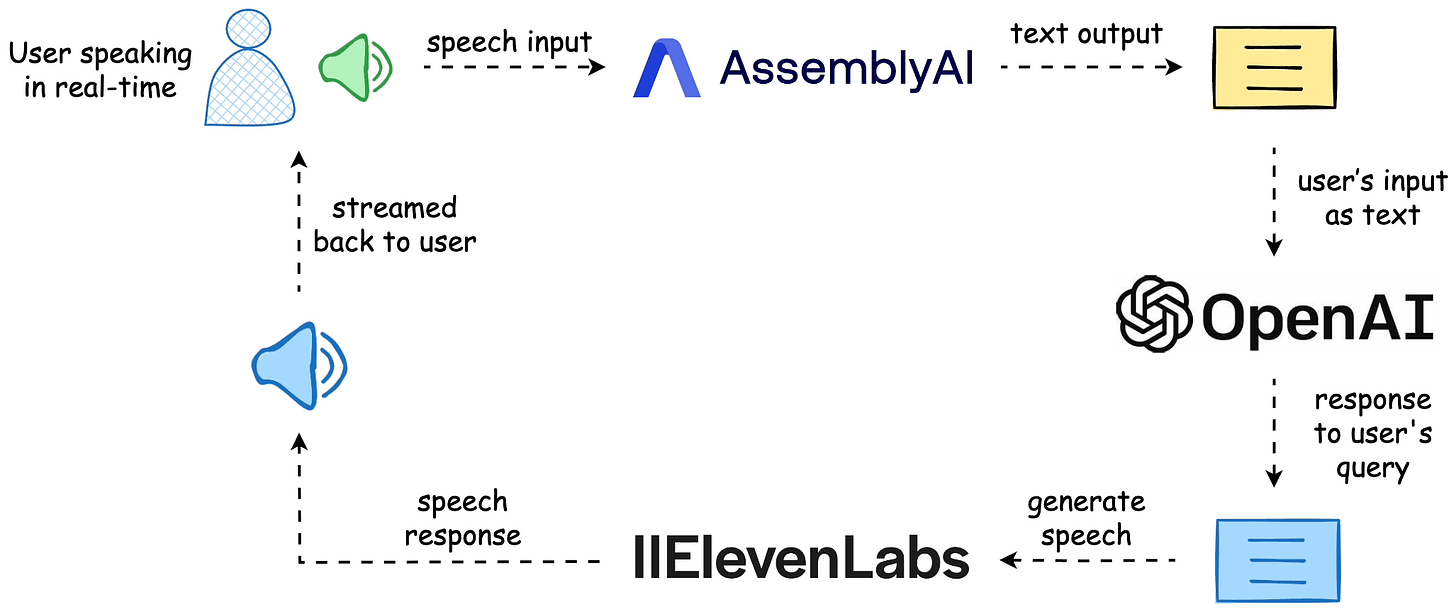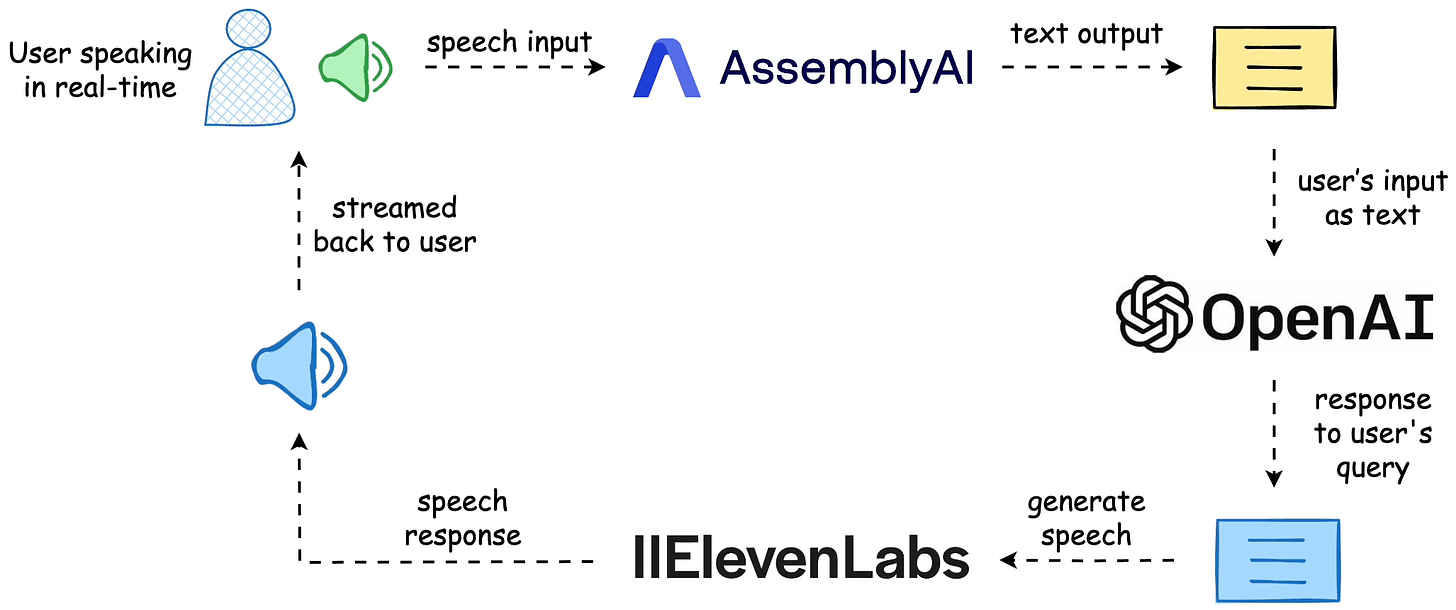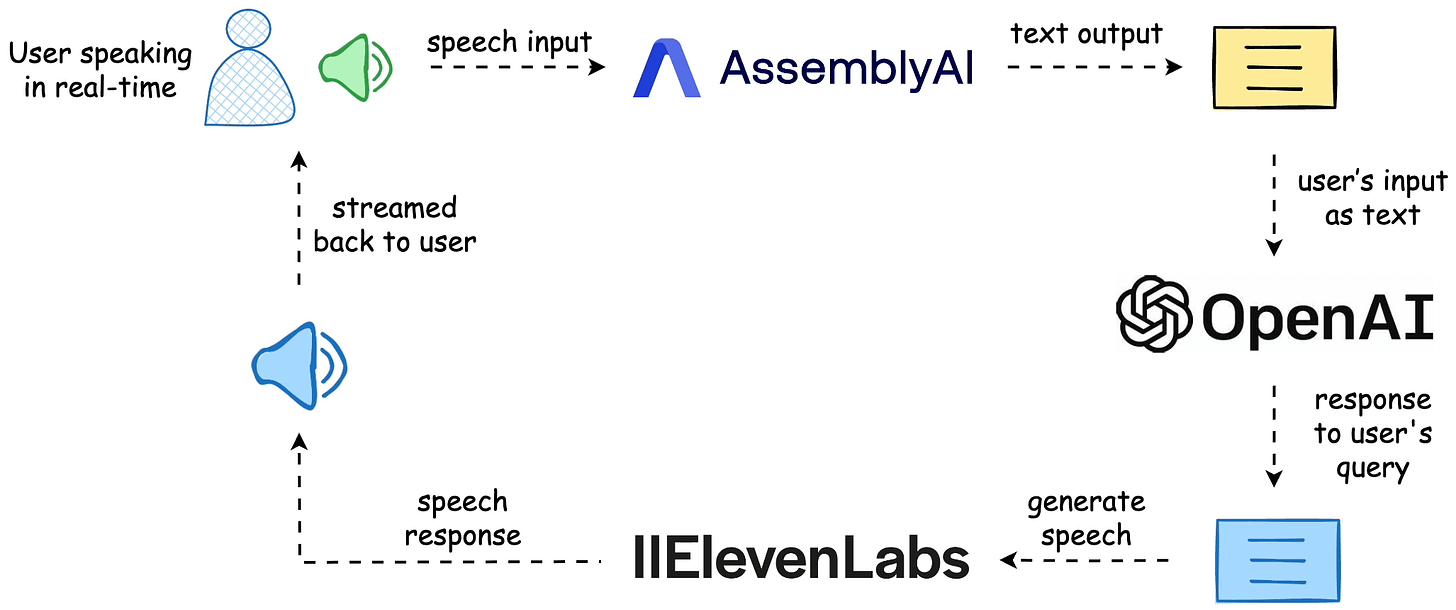
The workflow is depicted below, and the video above shows the final outcome.
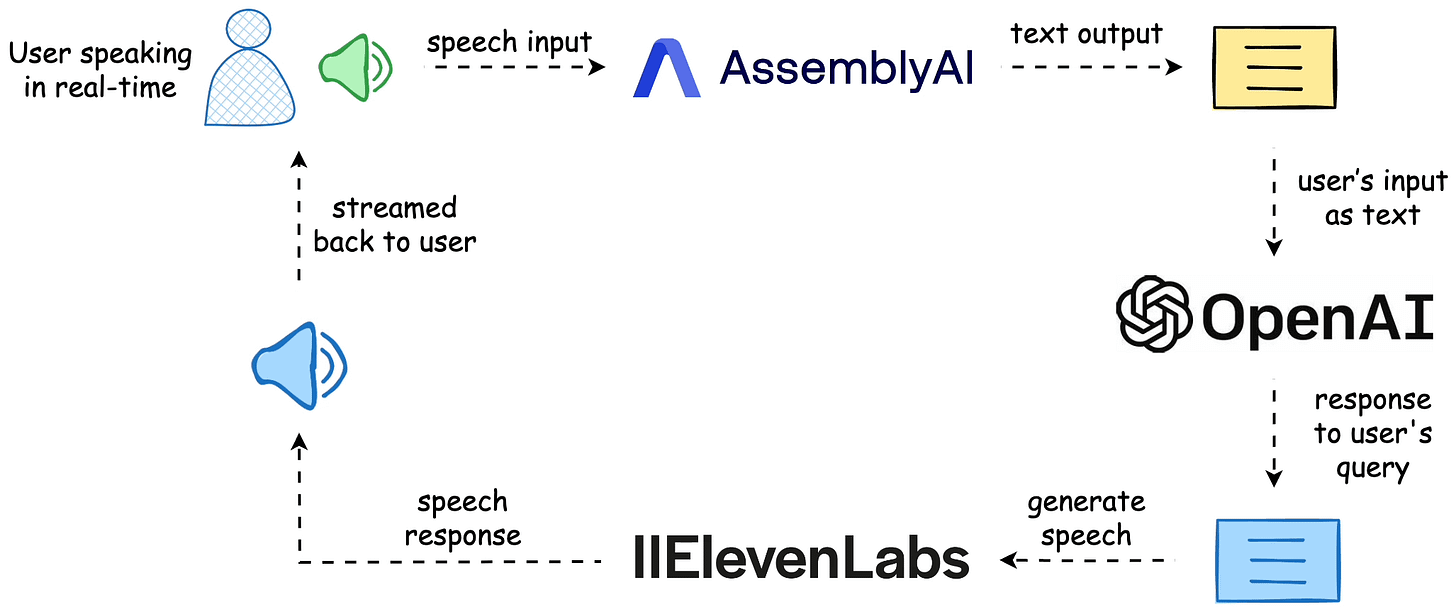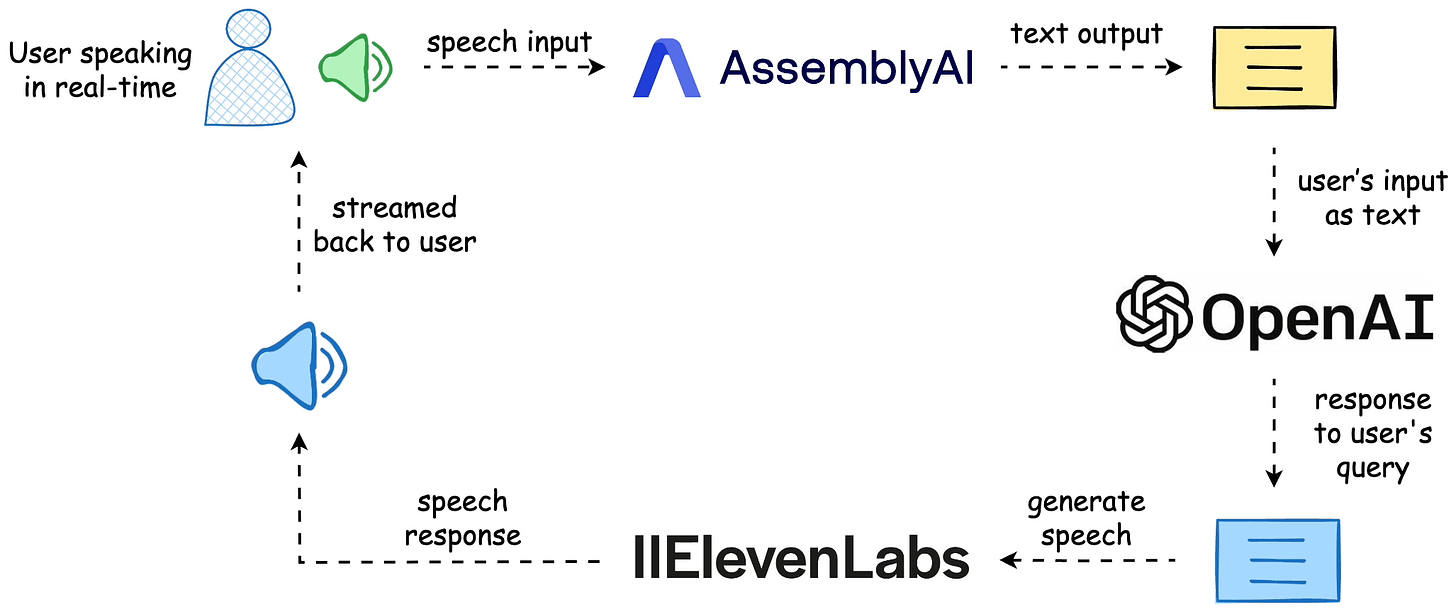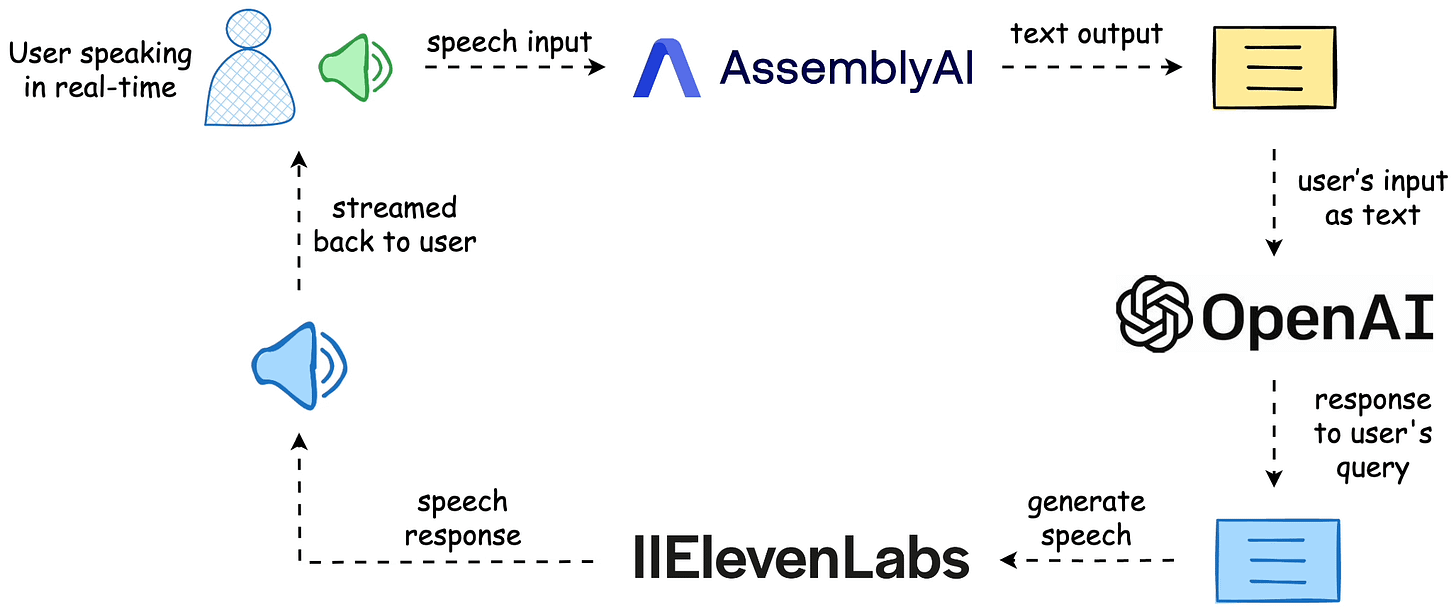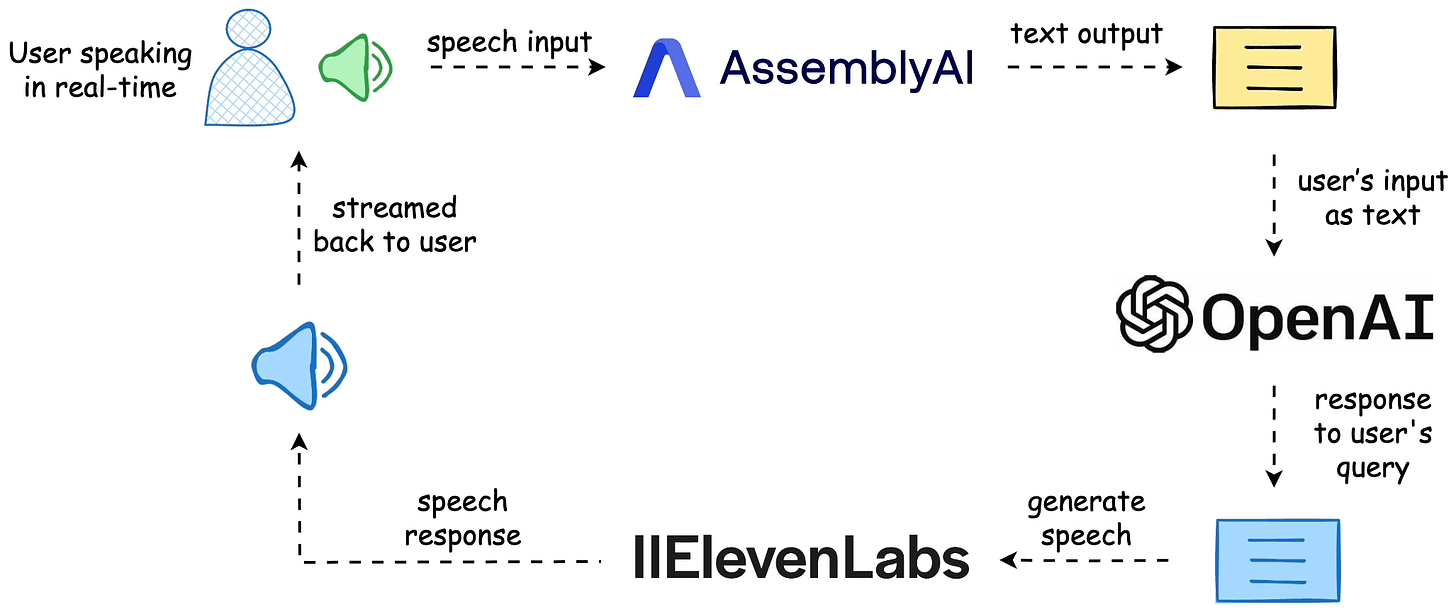
The entire code is available here: Voice Bot Demo GitHub.
Let’s build the app!
Start by installing the following libraries:

Next, create a file app.py and import the following libraries:
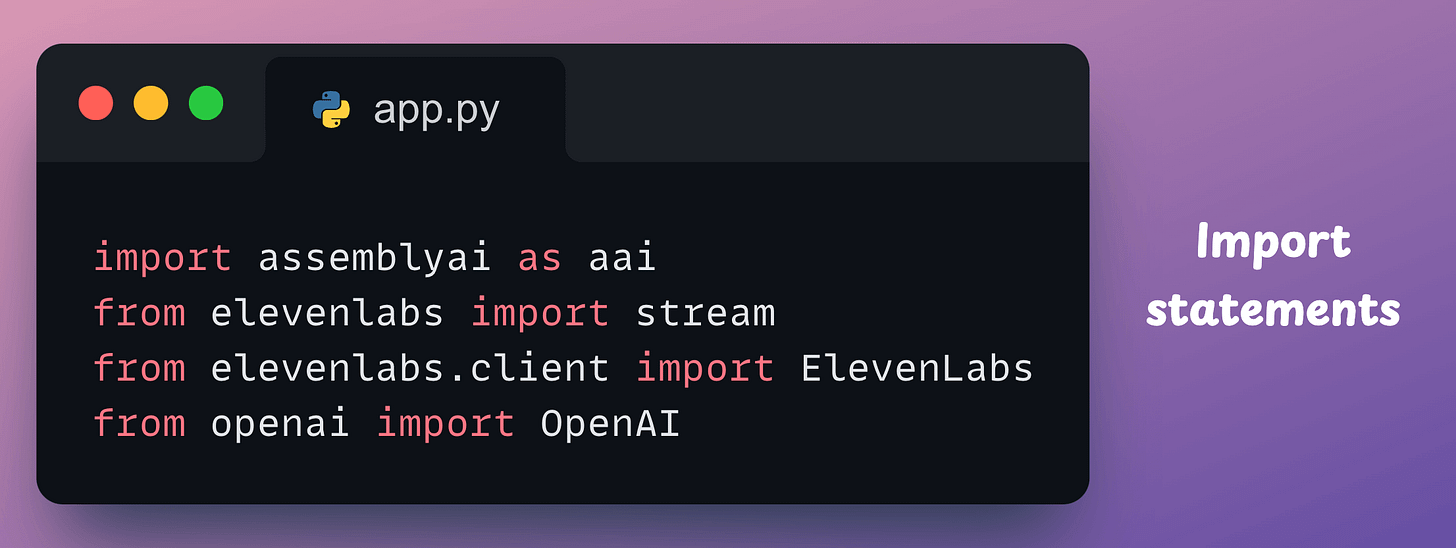
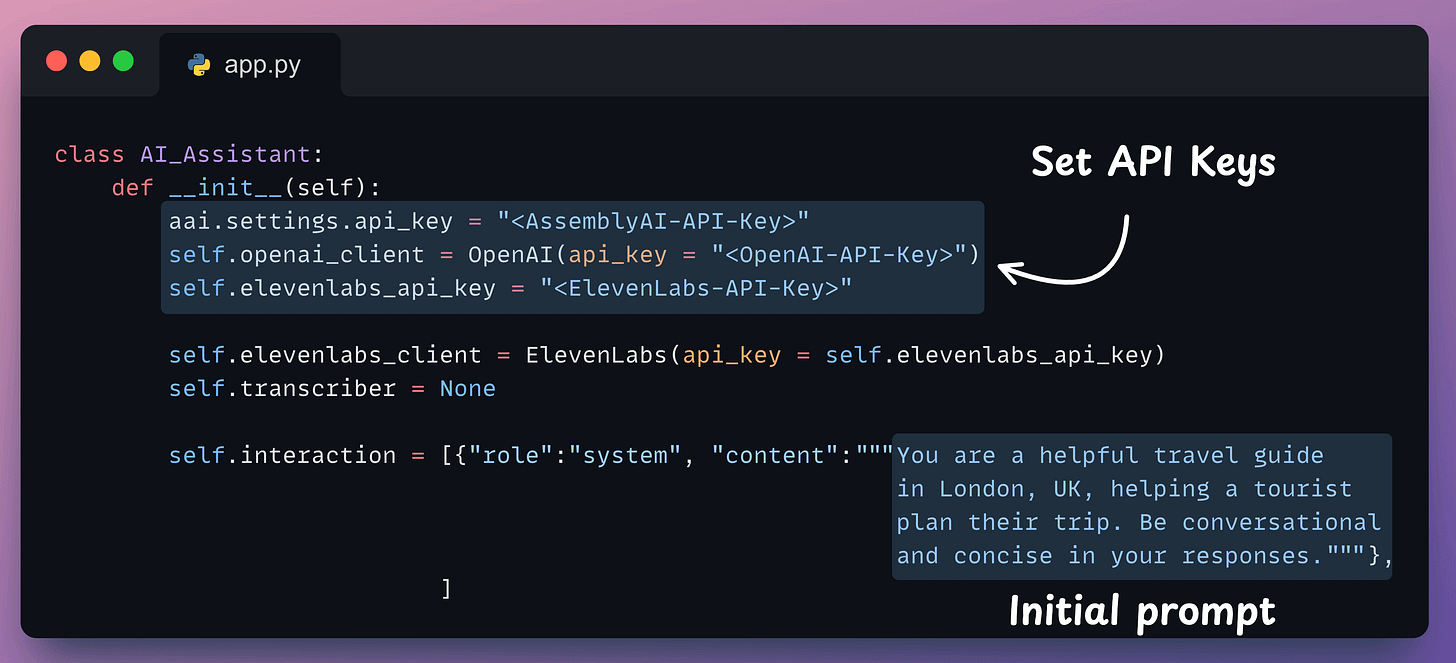
Next, we define a class, initialize the clients involved in our app—AssemblyAI, OpenAI, and ElevenLabs, and the interaction history:
Now think about the logical steps we would need to implement in this app:
self.interaction object defined in the __init__ method so that OpenAI has the entire context while producing a response in Step 3.Thus, we need at least four more methods in AI_Assistant class:
generate_audio → Accepts some text and uses ElevenLabs to verbalize it:
generate_ai_response → Accepts the transcribed input, adds it to the interaction, and sends it to OpenAI to produce a response. Finally, it should pass this response to the generate_audio method: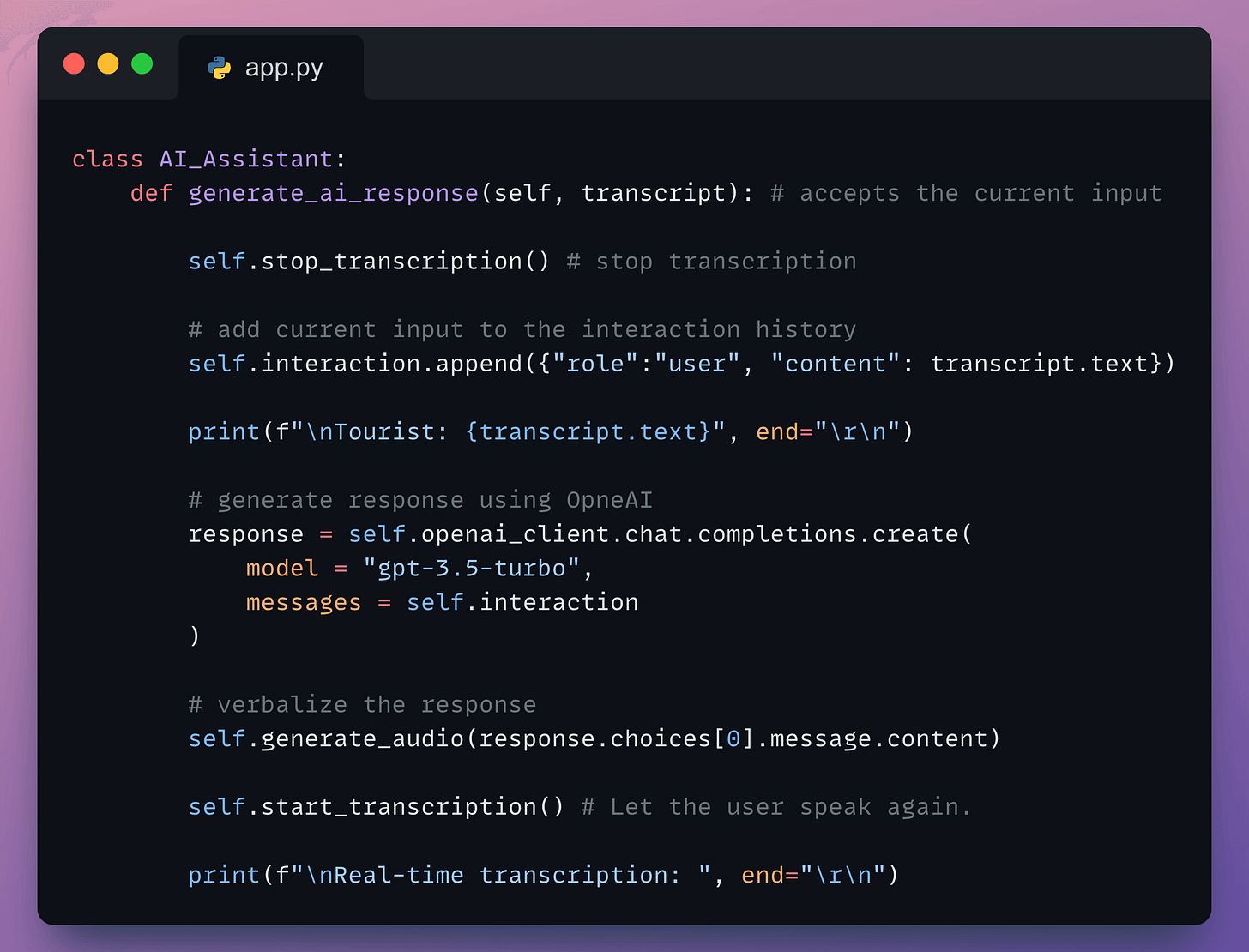
start_transcription → Starts the microphone to record audio and transcribe it in real-time with AssemblyAI: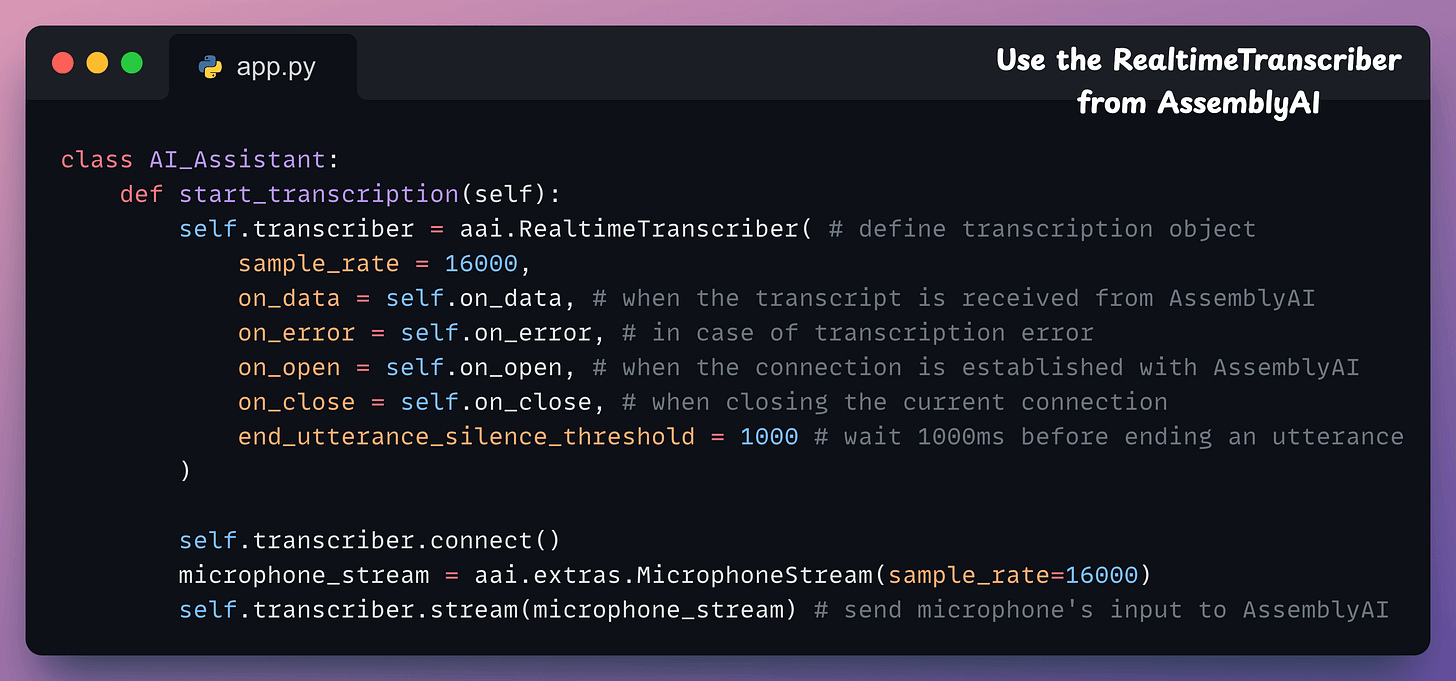
on_data → the method to invoke upon receiving a transcript from AssemblyAI. Here, we invoke the generate_ai_response method:on_error → the method to invoke in case of an error (you can also reinvoke the start_transcription method).on_open → the method to invoke when a connection has been established with AssemblyAI.on_close → the method to invoke when closing a connection.
stop_transcription → Stops the microphone and let the OpenAI generate a response using the method below.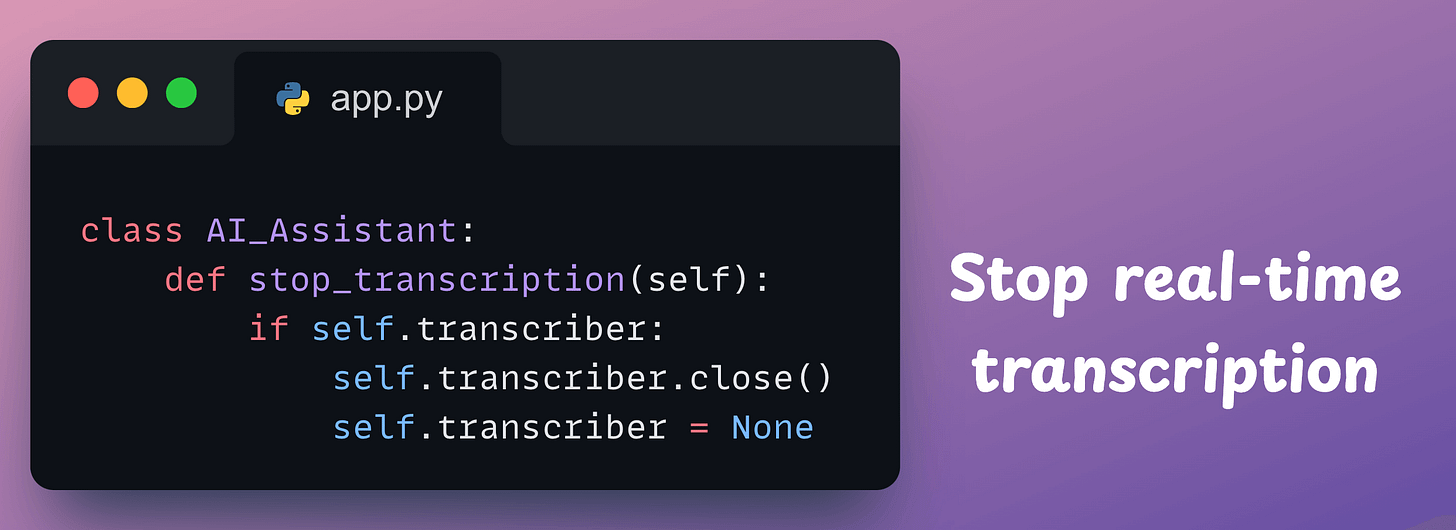
Done!
With that, we have implemented the class.
Finally, we instantiate an object of this class and start the app:

Done!
This produces the output shown in the video below:
That was simple, wasn’t it?
You can find all the code and instructions to run in this GitHub repo: Voice Bot Demo GitHub.
I first used AssemblyAI two years ago, and in my experience, it has the most developer-friendly and intuitive SDKs to integrate speech AI into applications.
AssemblyAI first trained Universal-1 on 12.5 million hours of audio, outperforming every other model in the industry (from Google, OpenAI, etc.) across 15+ languages.
Now, they released Universal-2, their most advanced speech-to-text model yet.
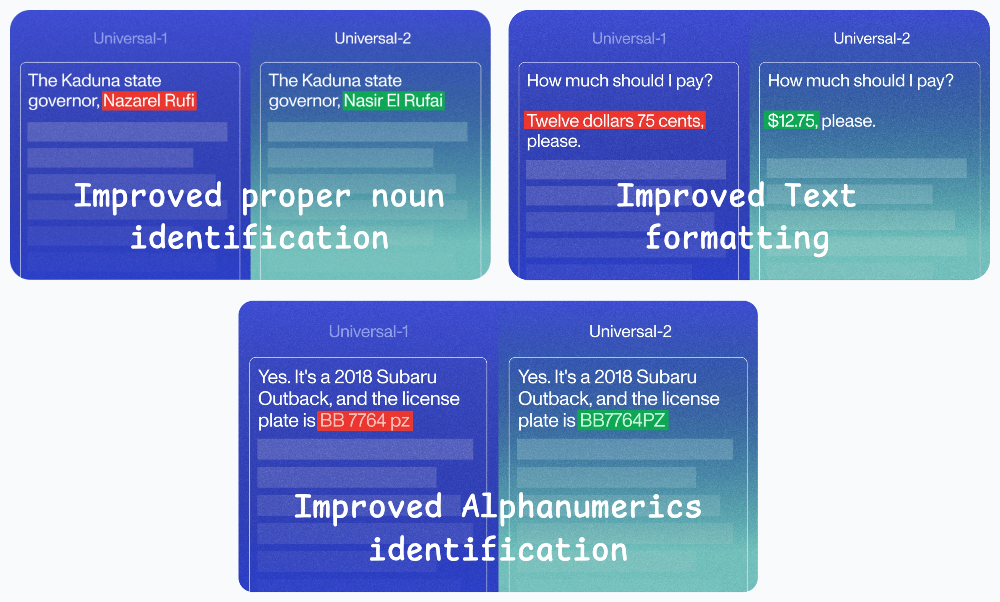
Here’s how Universal-2 compares with Universal-1:
Its performance compared to other popular models in the industry is shown below:
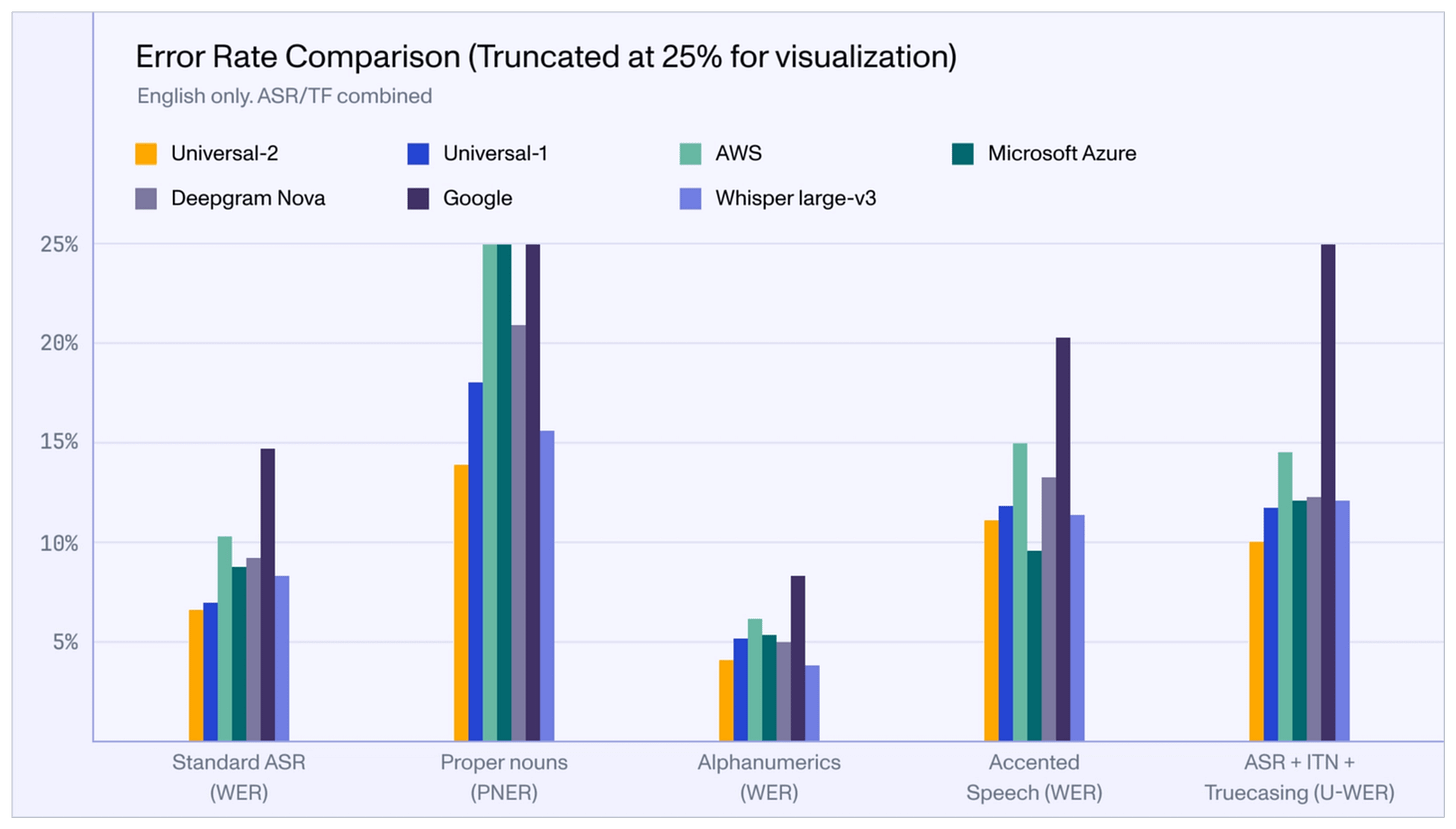
Isn’t that impressive?
I love AssemblyAI’s mission of supporting developers in building next-gen voice applications in the simplest and most effective way possible.
They have already made a big dent in speech technology, and I’m eager to see how they continue from here.
Get started with:

Their API docs are available here if you want to explore their services: AssemblyAI API docs.
🙌 Also, a big thanks to AssemblyAI, who very kindly partnered with us on this post and let us use their industry-leading AI transcription services.
👉 Over to you: What would you use AssemblyAI for?