Building a Browser Automation Agent
...explained visually and with code.

...explained visually and with code.


TODAY'S ISSUE
The browser is still the most universal interface, with 4.3 billion pages visited every day!
Today, let's do a demo on how we can completely automate it with a local stack:
System overview:
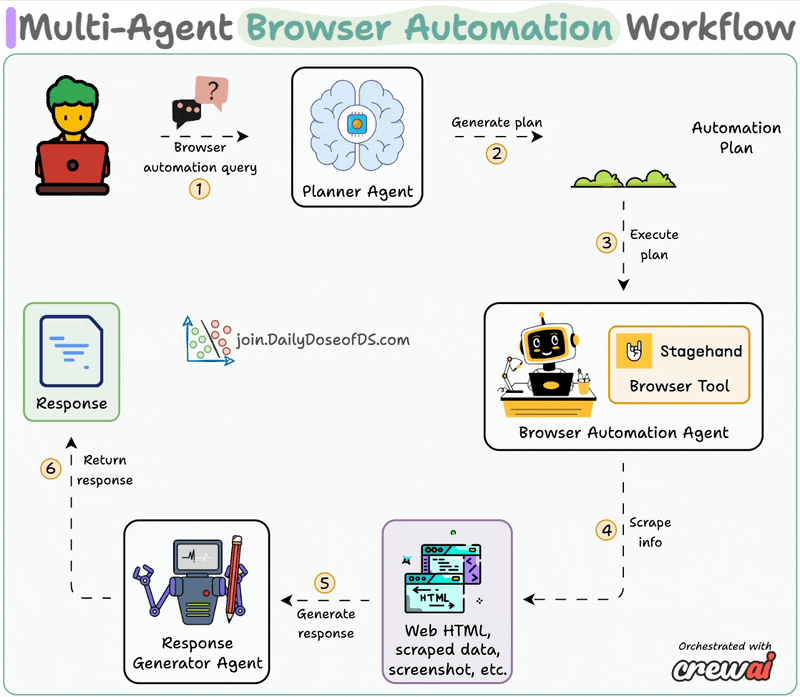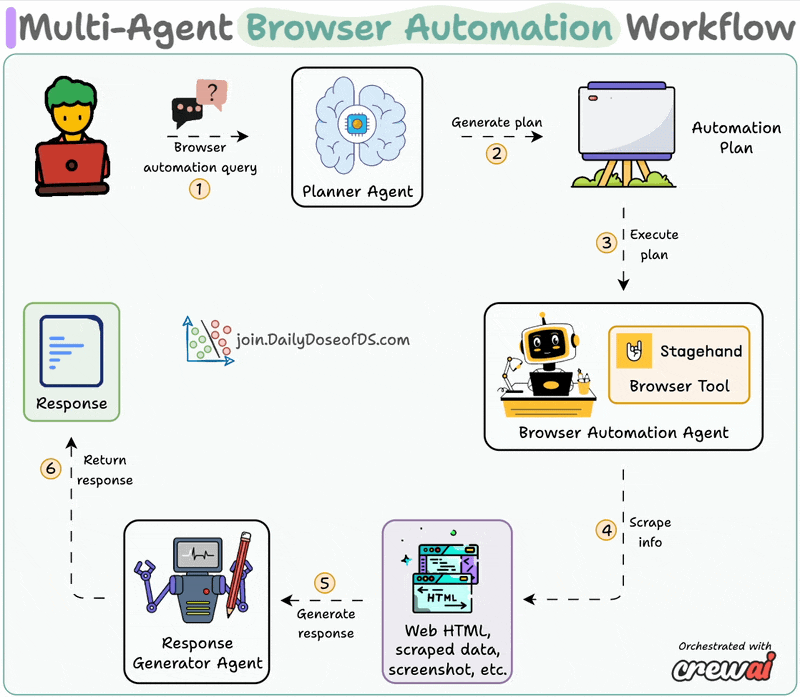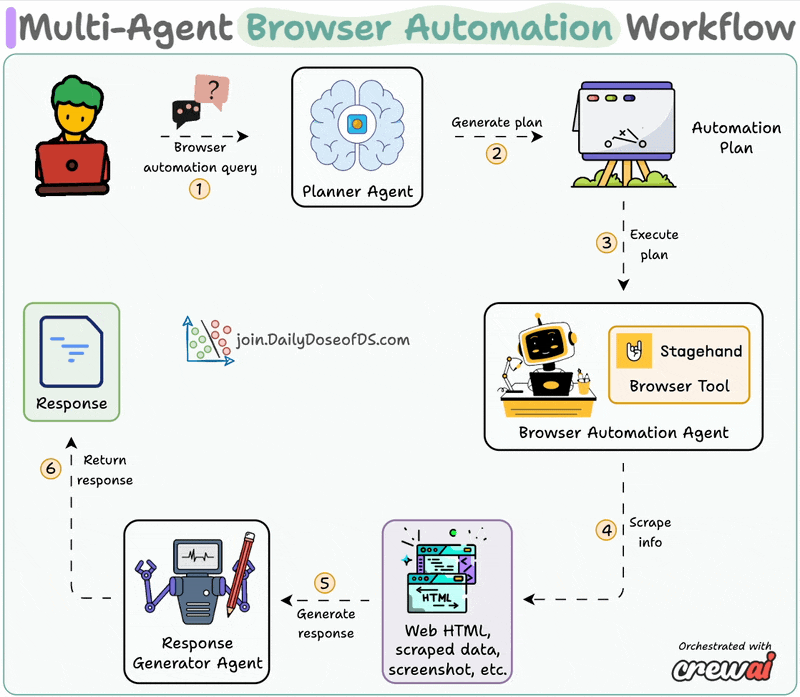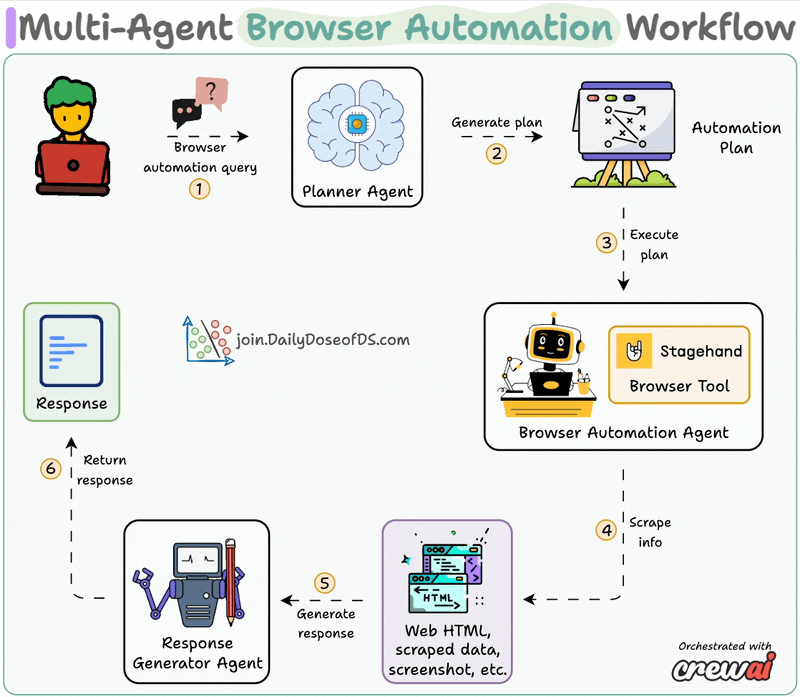
Now, let's dive into the code!
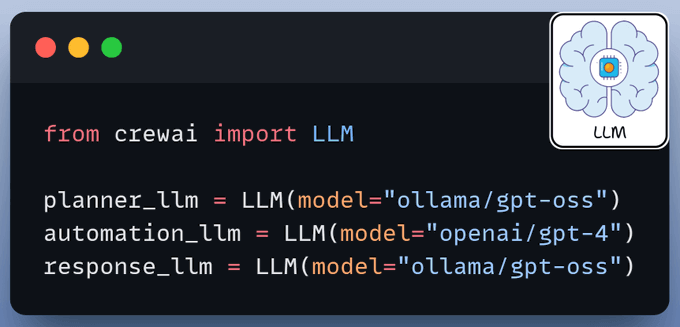
We use three LLMs:
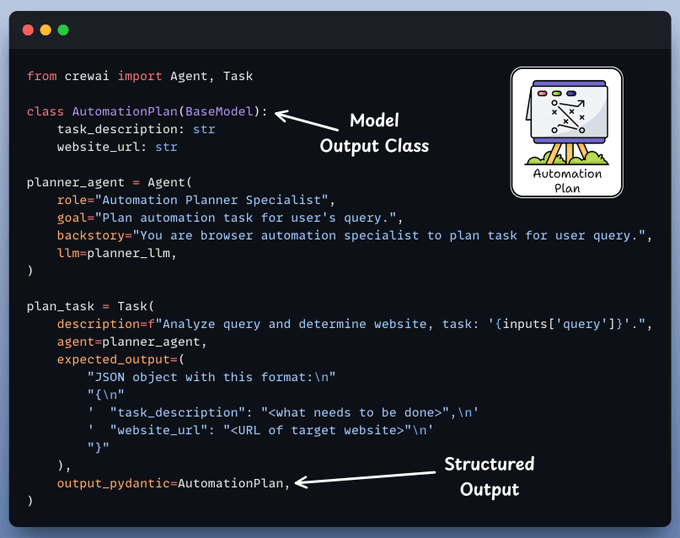
The planner agent receives an automation task from the user and creates a structured layout for execution by the browser agent.
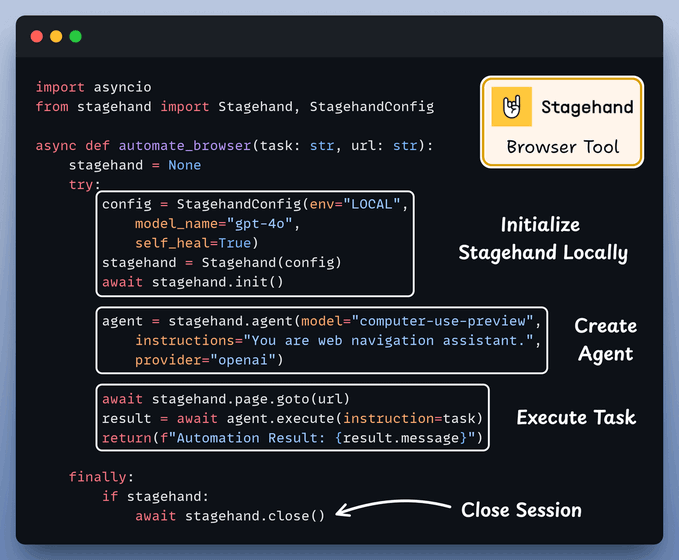
A custom CrewAI tool utilizes AI to interact with web pages.
It leverages Stagehand's computer-use agentic capabilities to autonomously navigate URLs, perform page actions, and extract data to answer questions.
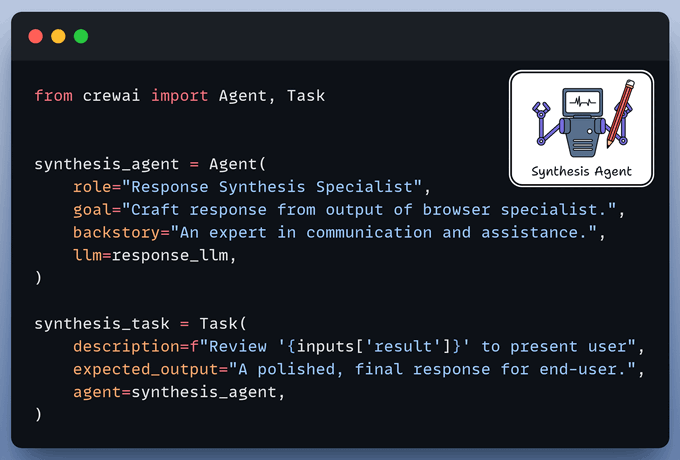
Browser Automation Agent utilizes the aforementioned Stagehand tool for autonomous browser control and plan execution.

Synthesis Agent acts as final quality control, refining output from the browser automation agent to generate a polished response.
Finally, we connect our Agents within a workflow using CrewAI Flows.
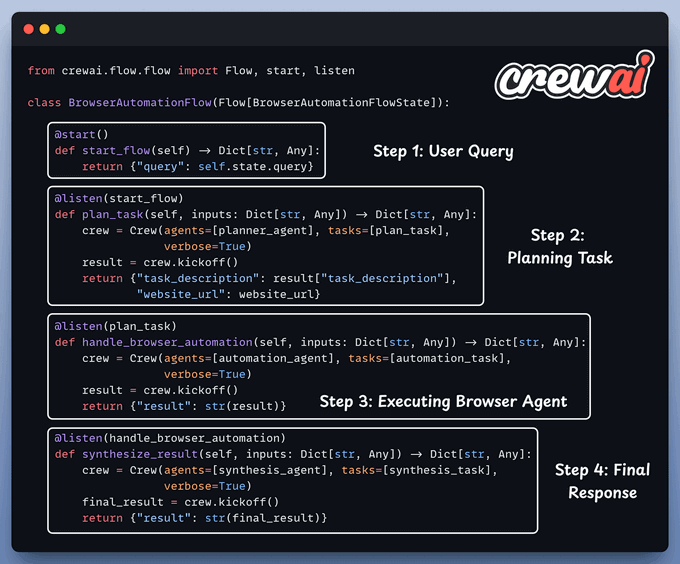
Done!
Here’s our multi-agent browser automation workflow in action, where we asked it to find the top contributor on the Stagehand GitHub repo:
It initiated a local browser session, navigated the web page, and extracted the information.
On paper, implementing a RAG system seems simple—connect a vector database, process documents, embed the data, embed the query, query the vector database, and prompt the LLM.
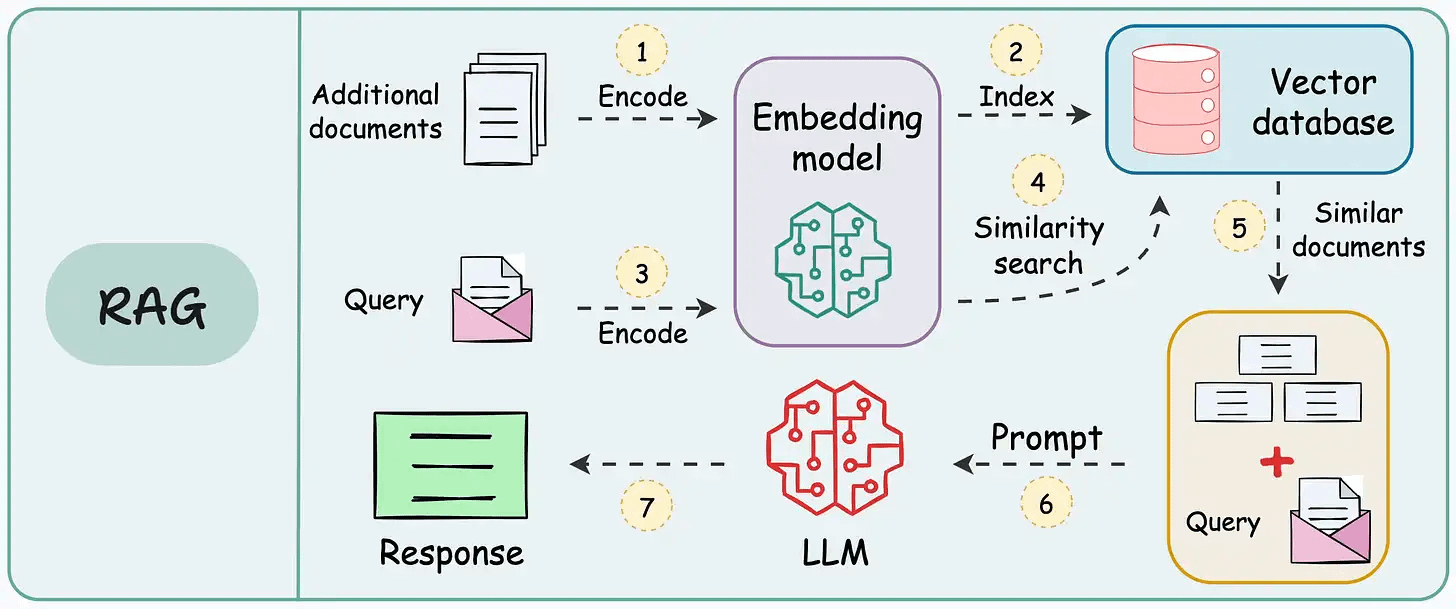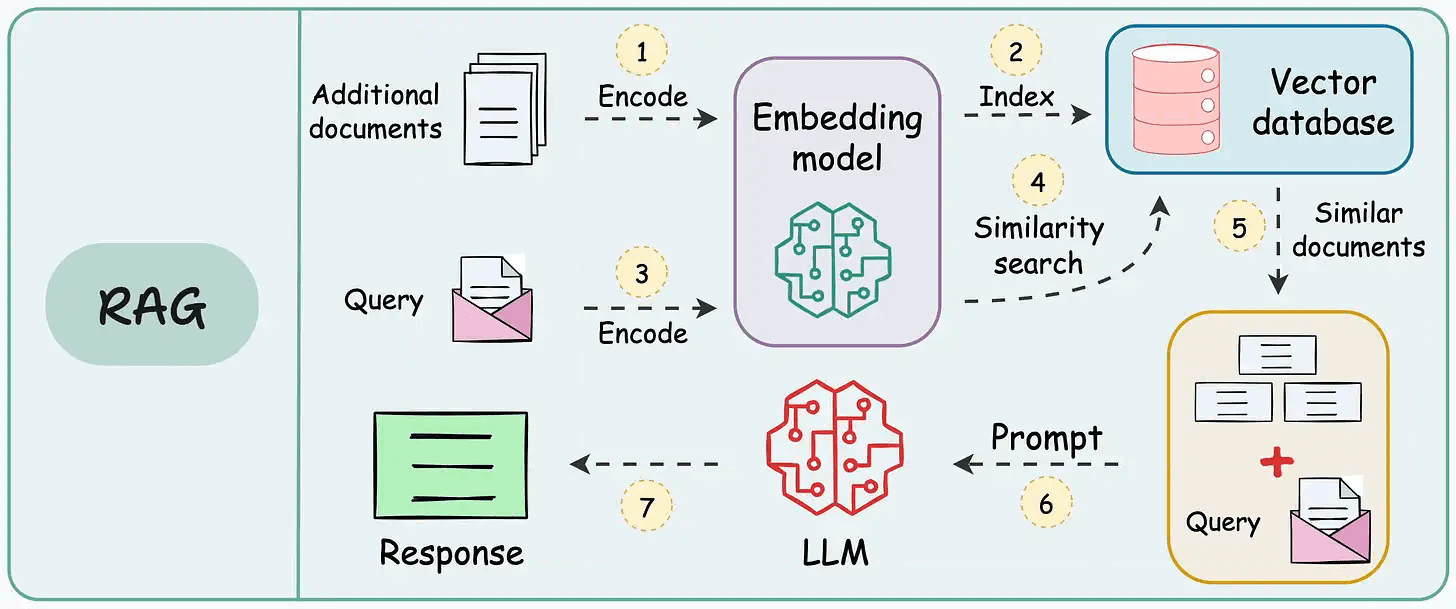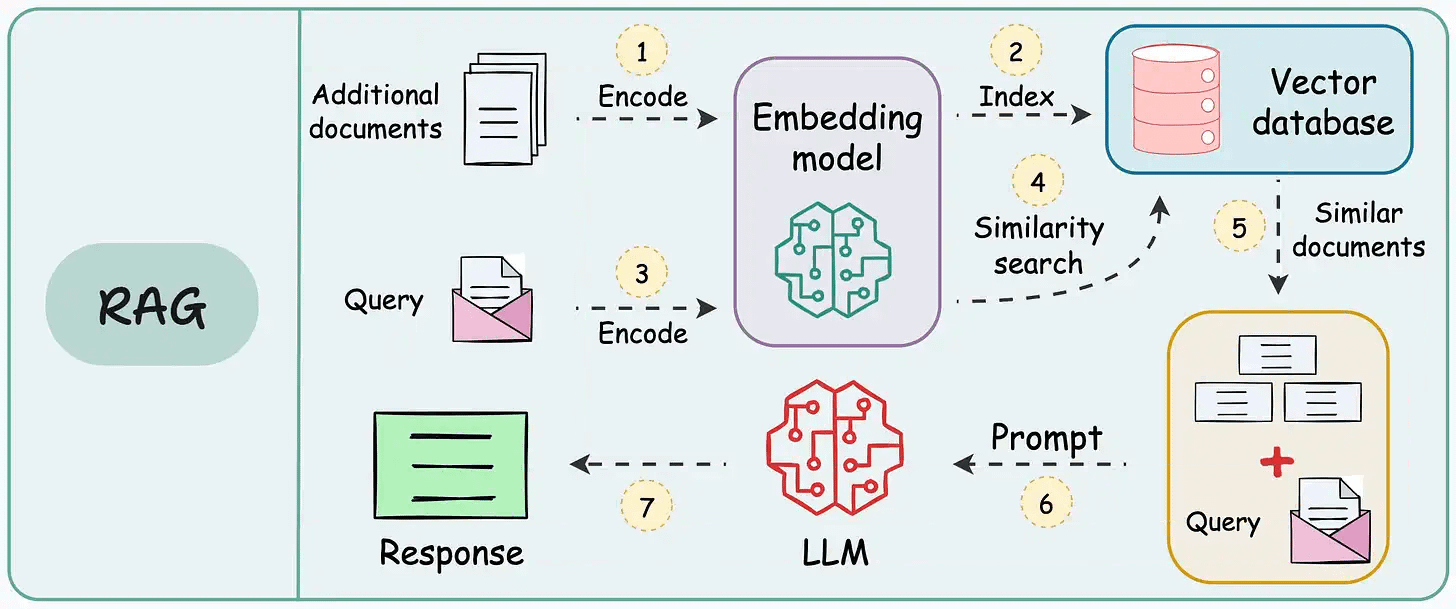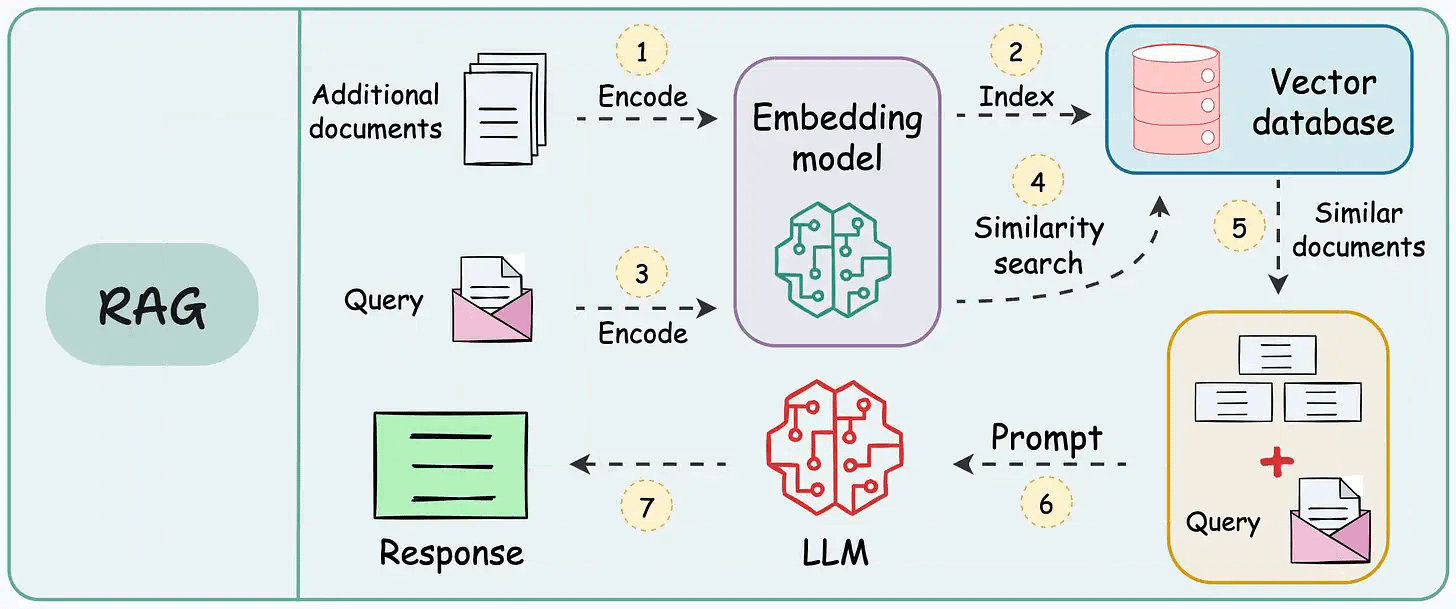
But in practice, turning a prototype into a high-performance application is an entirely different challenge.
We published a two-part guide that covers 16 practical techniques to build real-world RAG systems:
The list could go on since almost every major tech company I know employs graph ML in some capacity.
Becoming proficient in graph ML now seems to be far more critical than traditional deep learning to differentiate your profile and aim for these positions.
A significant proportion of our real-world data often exists (or can be represented) as graphs:
The field of graph neural networks (GNNs) intends to fill this gap by extending deep learning techniques to graph data.
Learn sophisticated graph architectures and how to train them on graph data in this crash course →