3 Techniques to Train An LLM Using Another LLM
Techniques used in DeepSeek, Llama 4, and Gemma.

Techniques used in DeepSeek, Llama 4, and Gemma.


TODAY'S ISSUE
LLMs don't just learn from raw text; they also learn from each other:
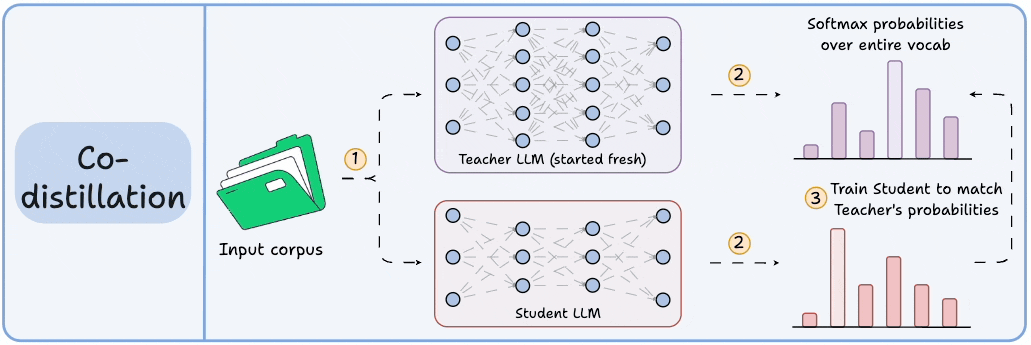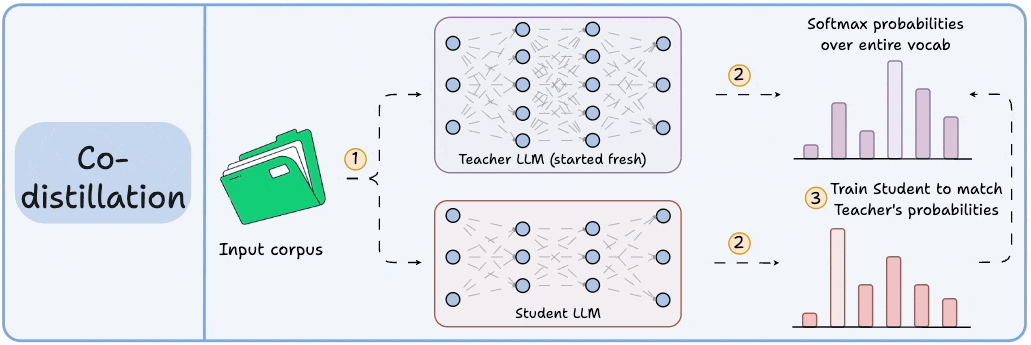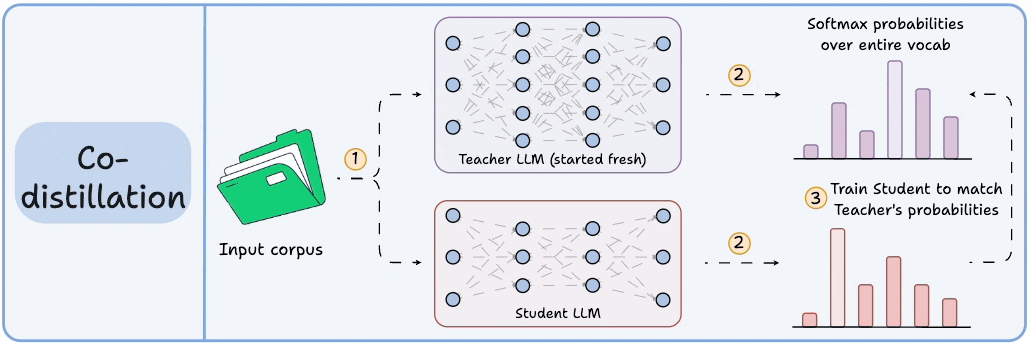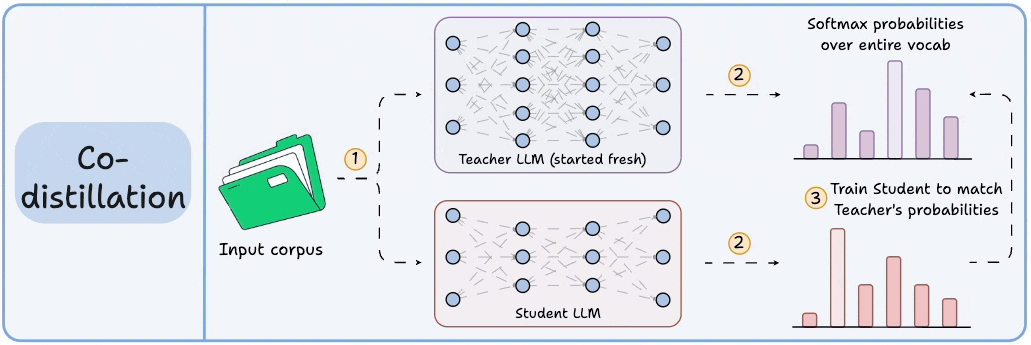
Distillation helps us do so, and the visual below depicts three popular techniques.
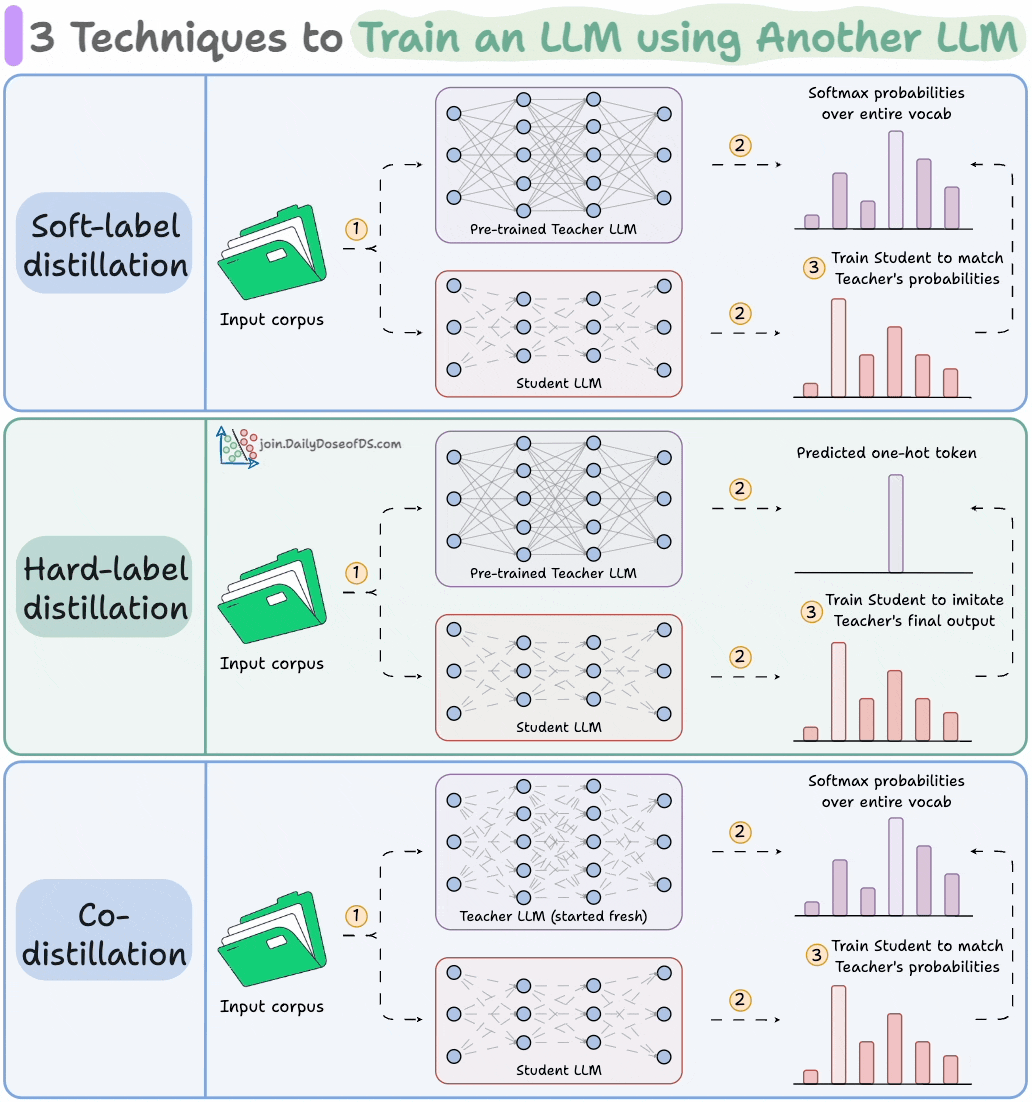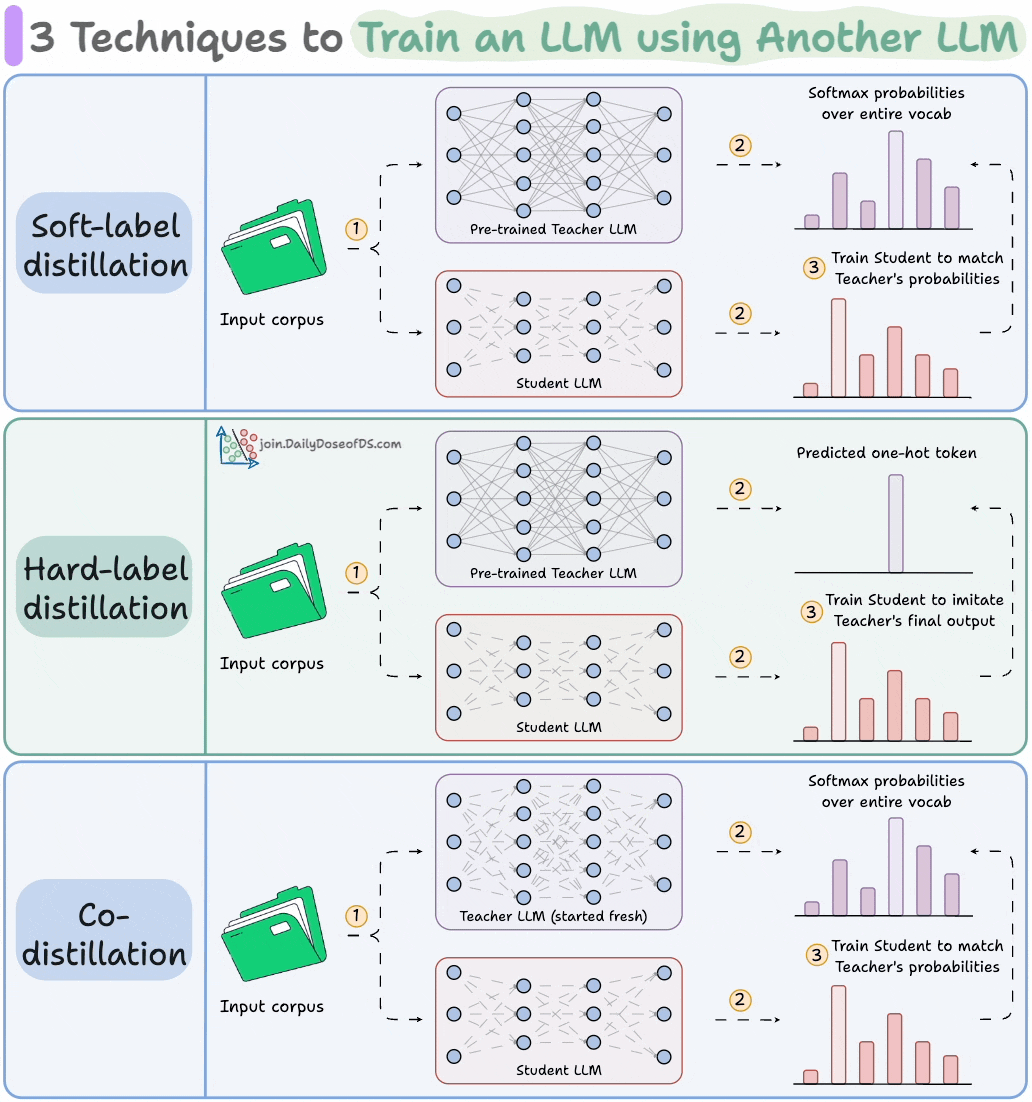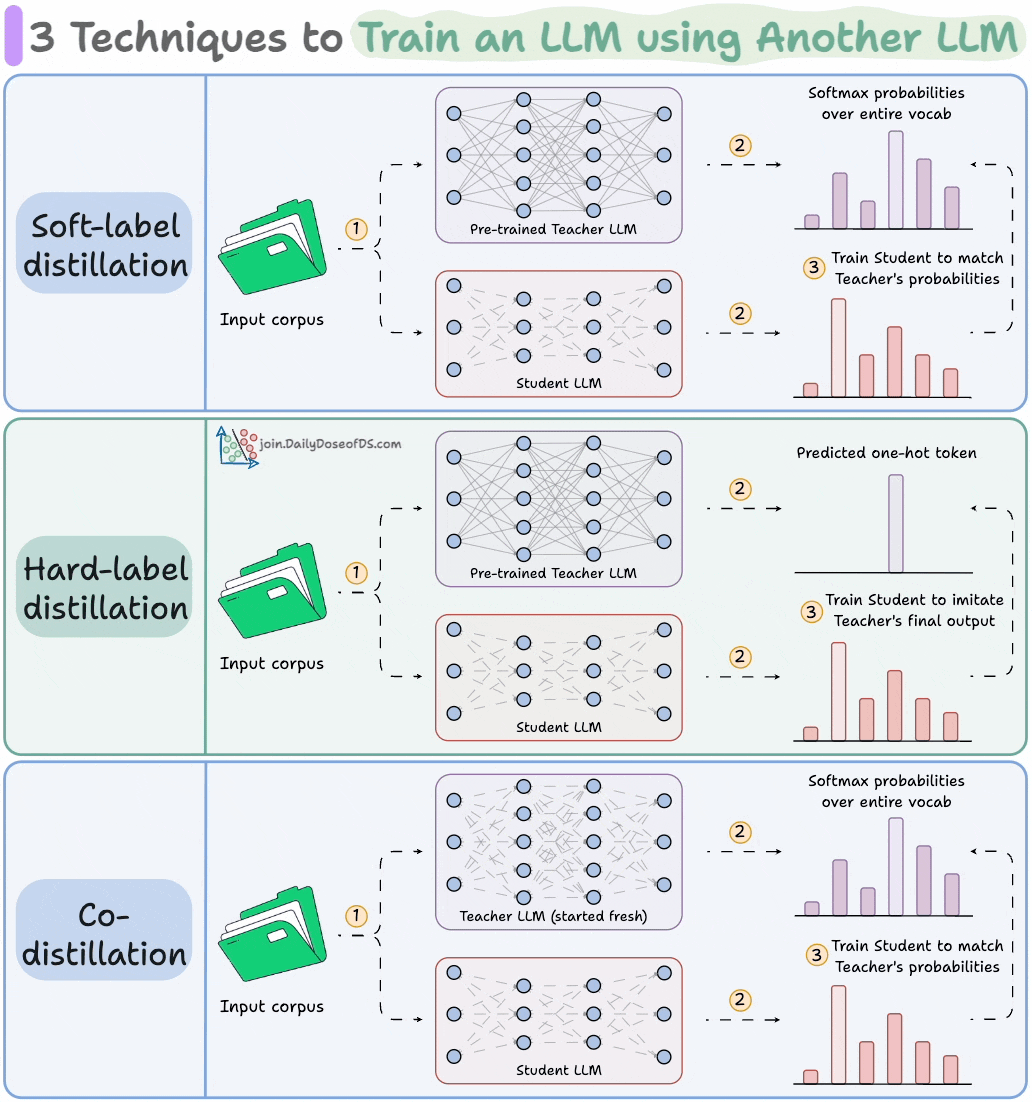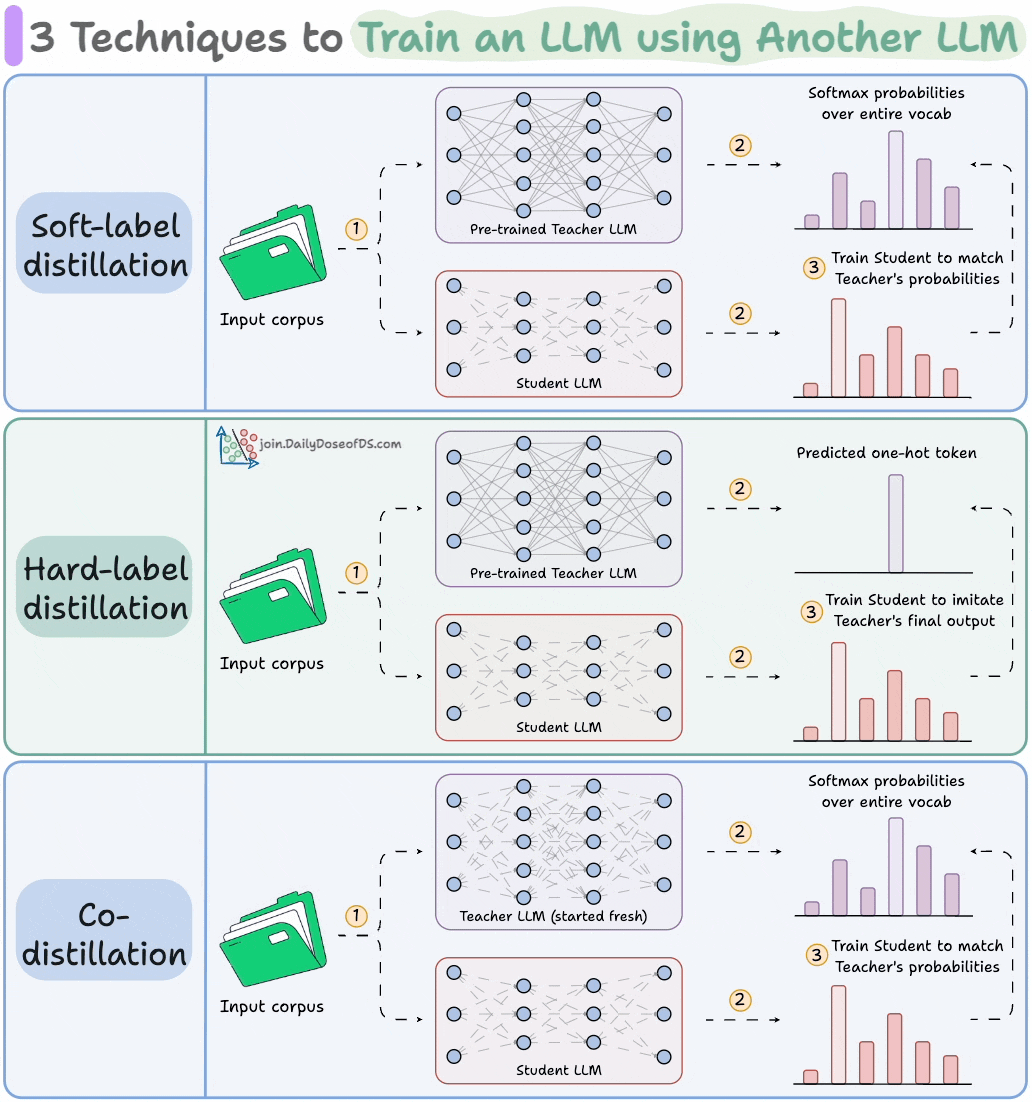
The idea is to transfer "knowledge" from one LLM to another, which has been quite common in traditional deep learning (like we discussed here).
Distillation in LLMs can happen at two stages:
1) Pre-training
2) Post-training:
You can also apply distillation during both stages, which Gemma 3 did.
Here are the three commonly used distillation techniques:
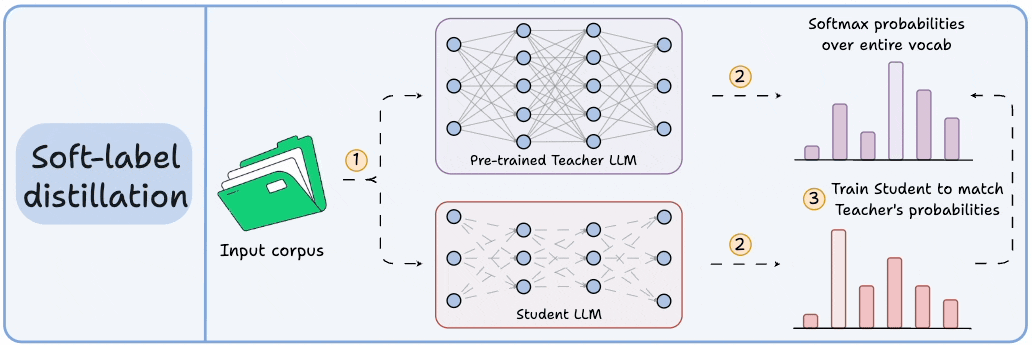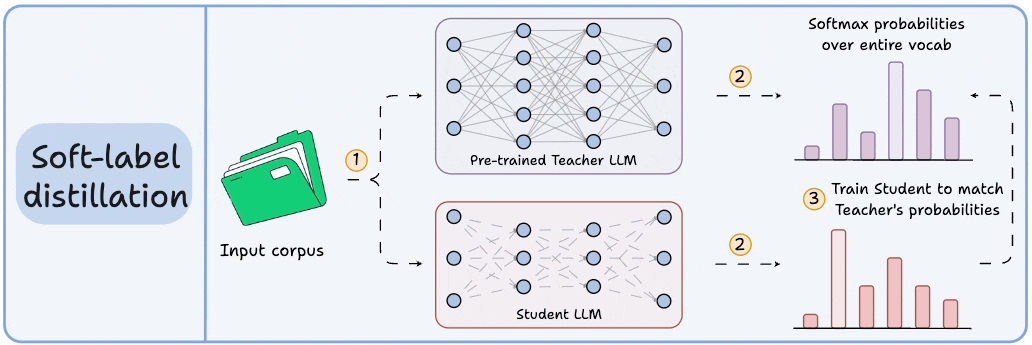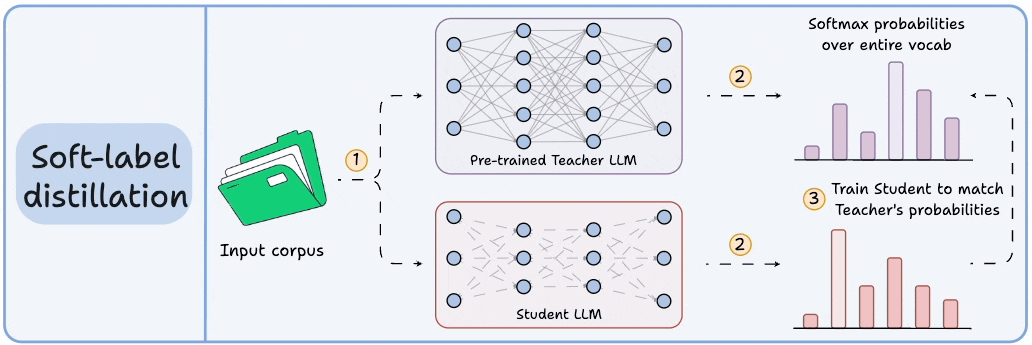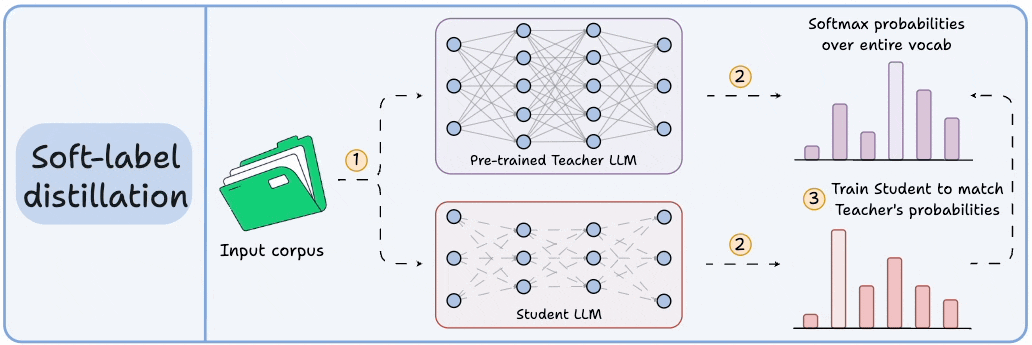
Visibility over the Teacher's probabilities ensures maximum knowledge (or reasoning) transfer.
However, you must have access to the Teacher’s weights to get the output probability distribution.
Even if you have access, there's another problem!
Say your vocab size is 100k tokens and your data corpus is 5 trillion tokens.
Since we generate softmax probabilities of each input token over the entire vocabulary, you would need 500 million GBs of memory to store soft labels under float8 precision.
The second technique solves this.
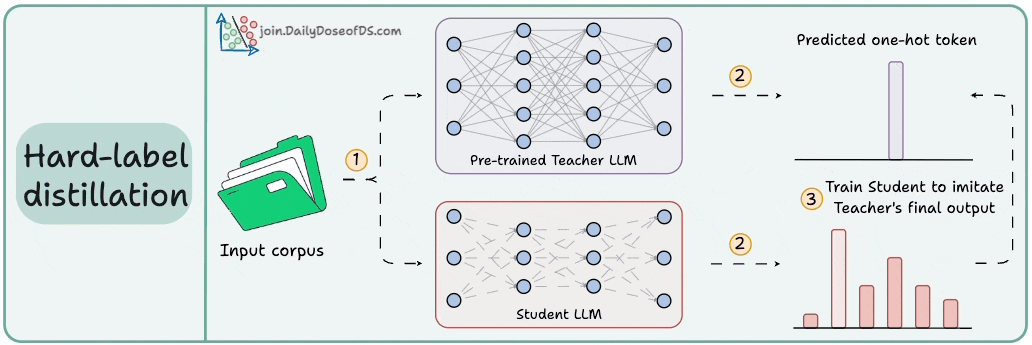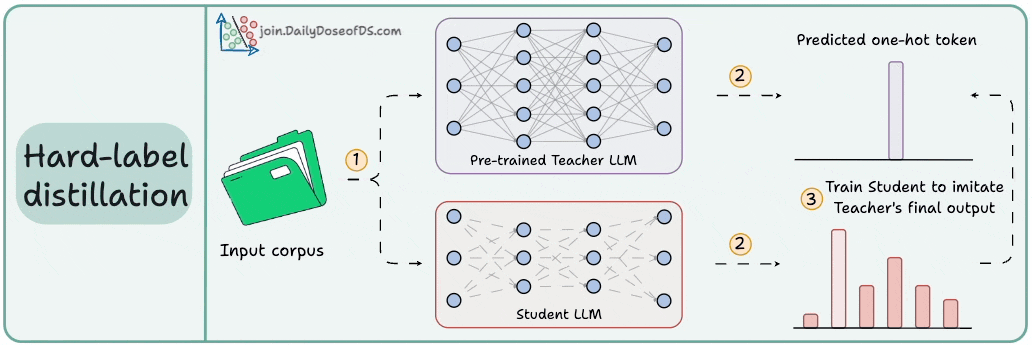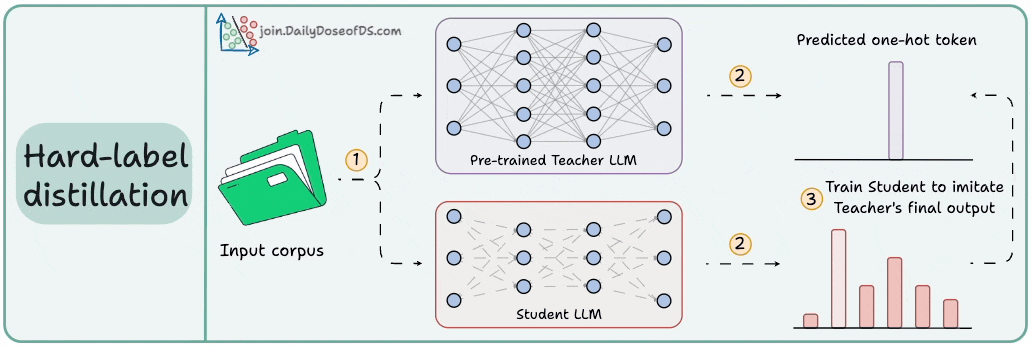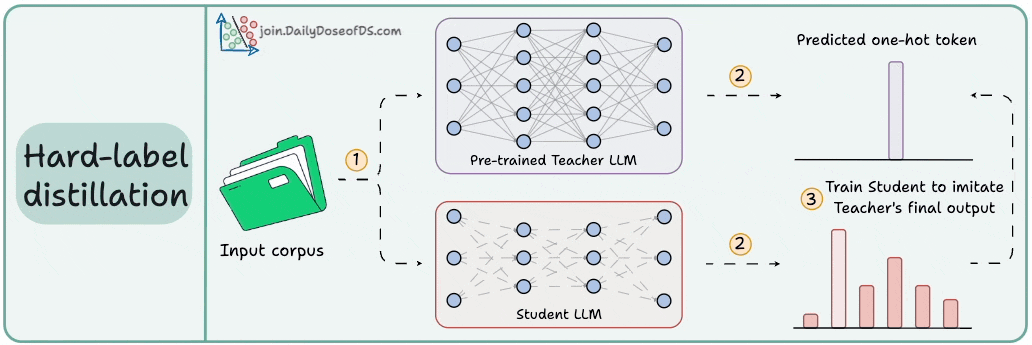
DeepSeek did this by distilling DeepSeek-R1 into Qwen and Llama 3.1 models.
Llama 4 did this to train Llama 4 Scout and Maverick from Llama 4 Behemoth.
Of course, during the initial stages, soft labels of the Teacher LLM won't be accurate.
That is why Student LLM is trained using both soft labels + ground-truth hard labels.
👉 Over to you: Which technique do you find the most promising?
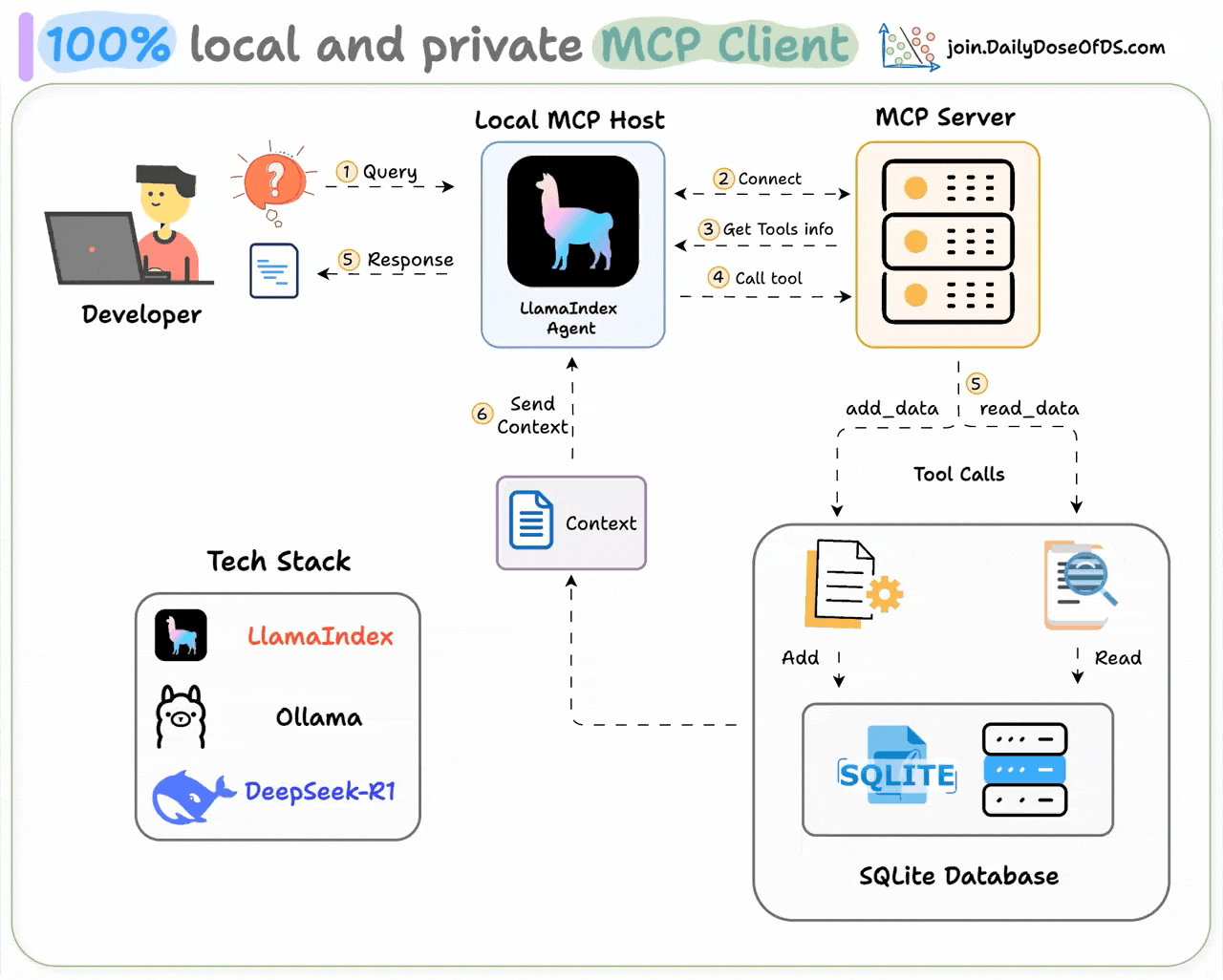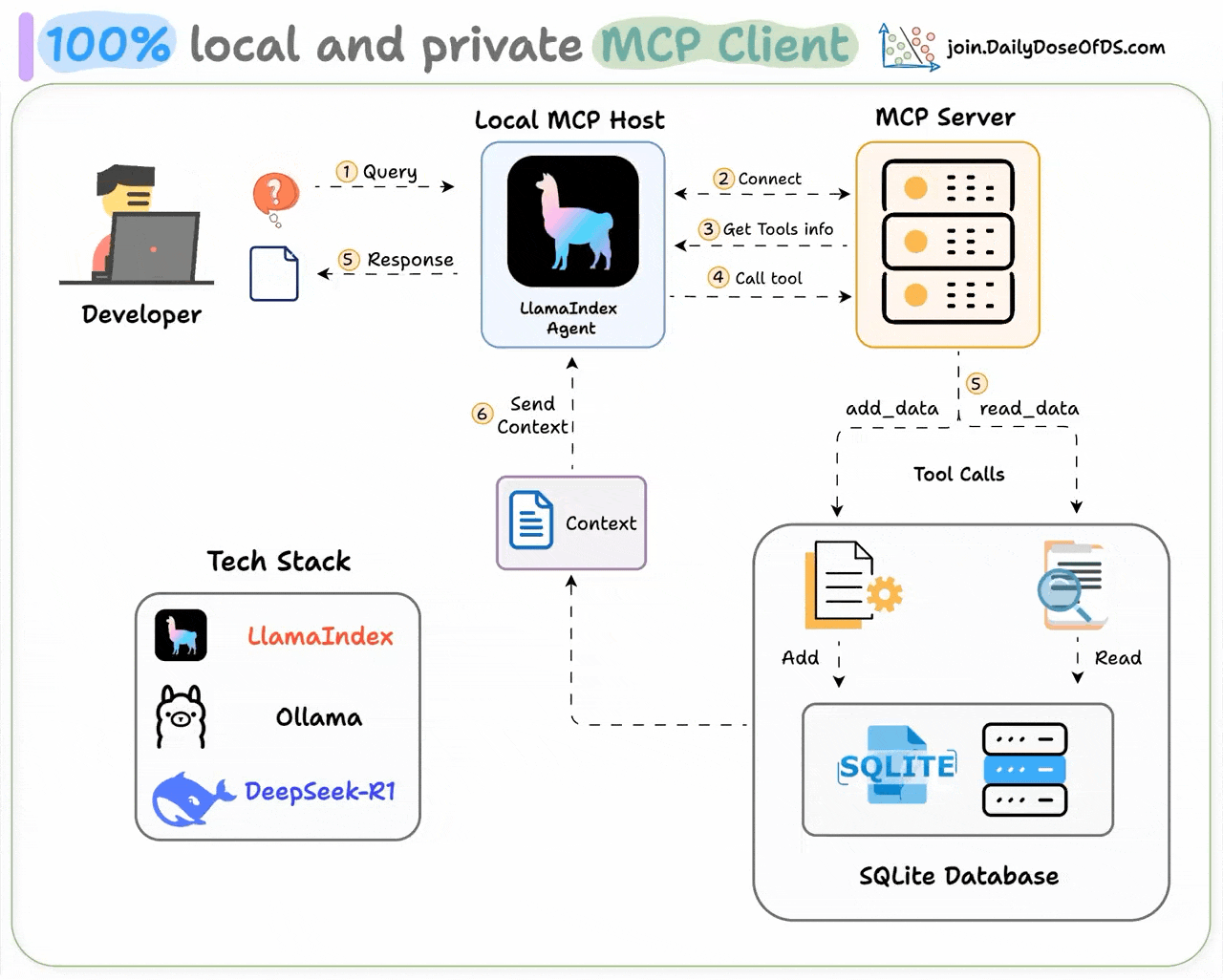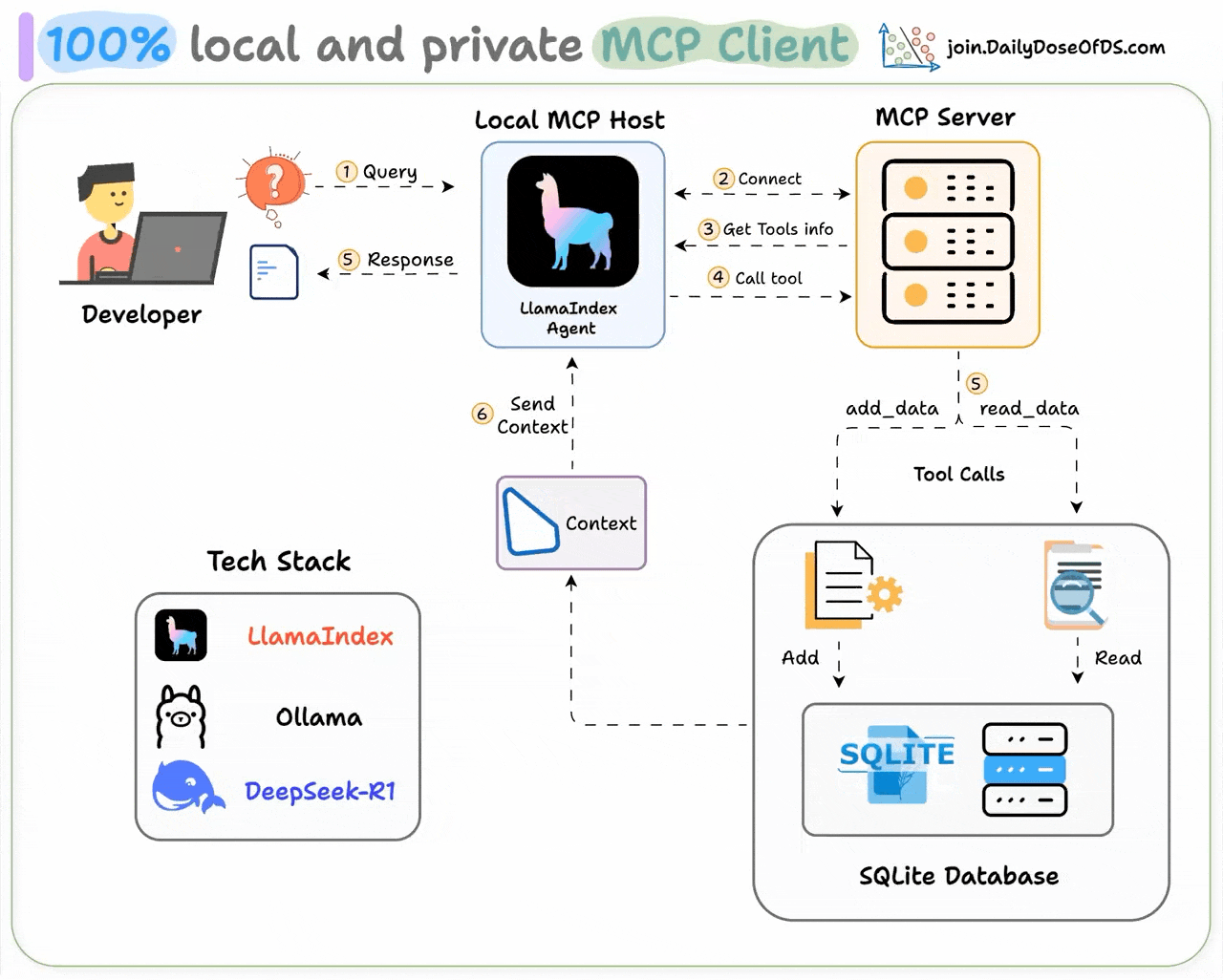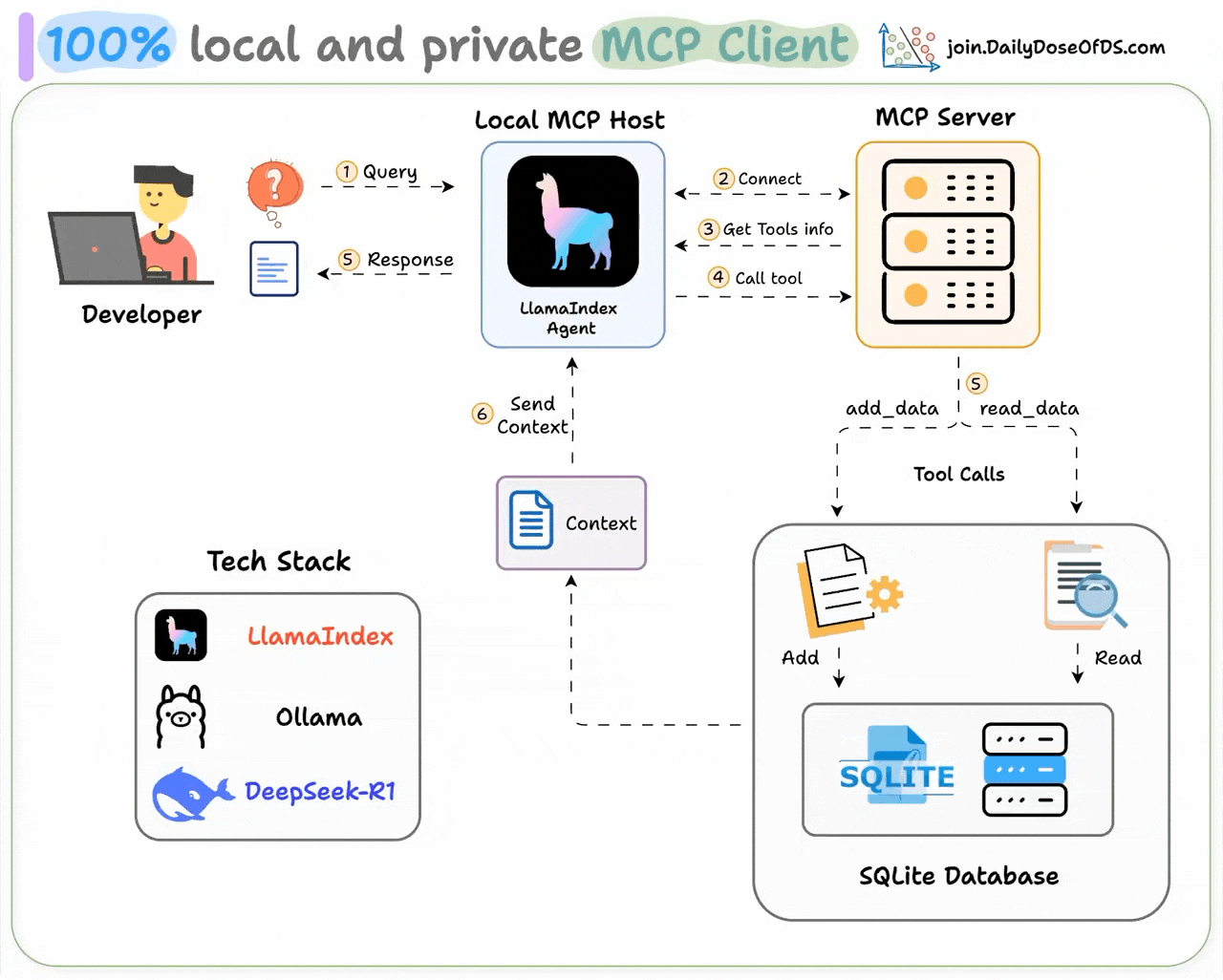
An MCP client is a component within an AI application (like Cursor) that establishes standardized connections to external tools and data sources via the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
Recently, we built one 100% locally and explained the process in this video:
Tech stack:
Here's our workflow: