Course content
-
MLOpsx Lessons
- Background and Foundations for ML in Production
- The Machine Learning System Lifecycle
- Reproducibility and Versioning in ML Systems: Fundamentals of Repeatable and Traceable Setups
- Reproducibility and Versioning in ML Systems: Weights and Biases for Reproducible ML
- Data and Pipeline Engineering: Data Sources, Formats, and ETL Foundations
- Data and Pipeline Engineering: Sampling, Data Leakage, and Feature Stores
- Data and Pipeline Engineering: Distributed Processing and Workflow Orchestration
- Model Development and Optimization: Fundamentals of Development and Hyperparameter Tuning
- Model Development and Optimization: Fine-Tuning, Pruning, and Efficiency
- Model Development and Optimization: Compression and Portability
- Model Deployment: Serialization, Containerization and API for Inference
- Model Deployment: Kubernetes
- Model Deployment: Cloud Fundamentals
- Model Deployment: Introduction to AWS
- Model Deployment: EKS Lifecycle and Model Serving
- Monitoring and Observability: Core Fundamentals
- Monitoring and Observability: Practical Tooling with Evidently, Prometheus, and Grafana
- CI/CD Workflows
-
LLMOpsx Lessons
- Foundations of AI Engineering and LLMs
- Building Blocks of LLMs: Tokenization and Embeddings
- Building Blocks of LLMs: Attention, Architectural Designs and Training
- Building Blocks of LLMs: Decoding, Generation Parameters, and the LLM Application Lifecycle
- Context Engineering: Foundations, Categories, and Techniques of Prompt Engineering
- Context Engineering: Prompt Management, Defense, and Control
- Context Engineering: An Introduction to the Information Environment for LLMs
- Context Engineering: Memory and Temporal Context
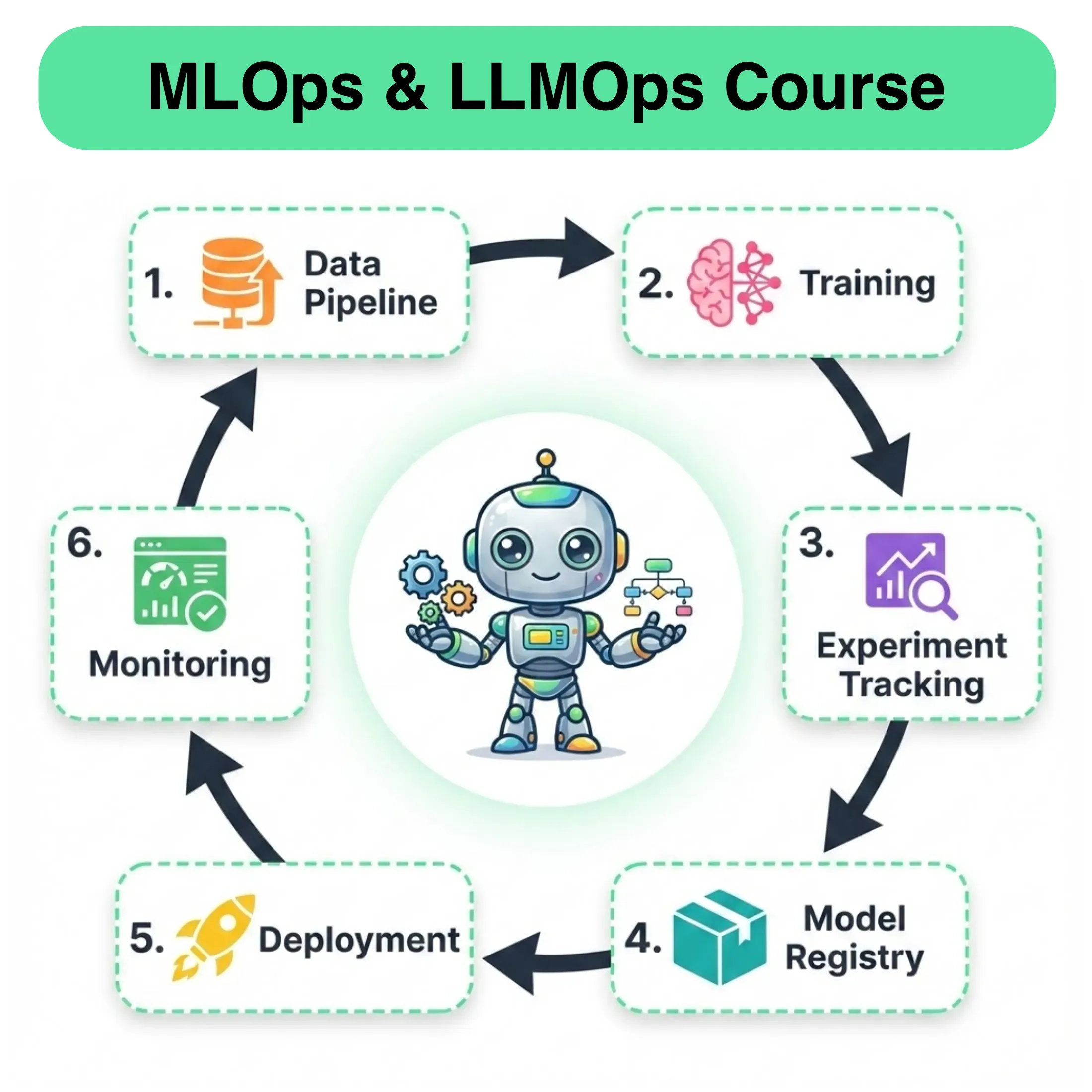
What happens once you have trained your ML model and tested its inference capabilities?
Is the job done?
Not really.
What you’ve completed is only a small part of a much larger journey that will unfold next.
If you plan to deploy the model in a real-world application, there are many additional steps to consider. This is where MLOps becomes essential, helping you transition from model development to a production-ready system.
It’s where ML meets software engineering, DevOps, and data engineering.
The goal is to reliably deliver ML-driven features (like recommendation engines, fraud detectors, voice assistants, etc.) to end-users at scale.
Hence, as mentioned earlier, a key realization is that the only a tiny fraction of an “ML system” is the ML code; the vast surrounding infrastructure (for data, configuration, automation, serving, monitoring, etc.) is much larger and more complex:
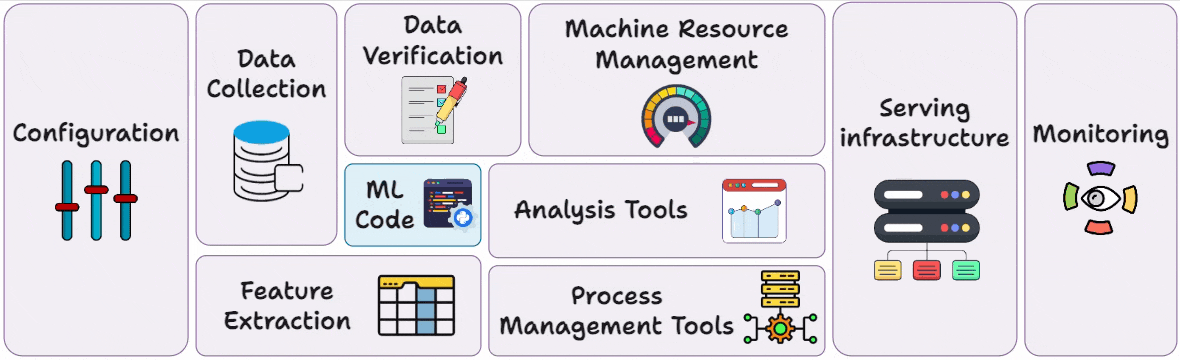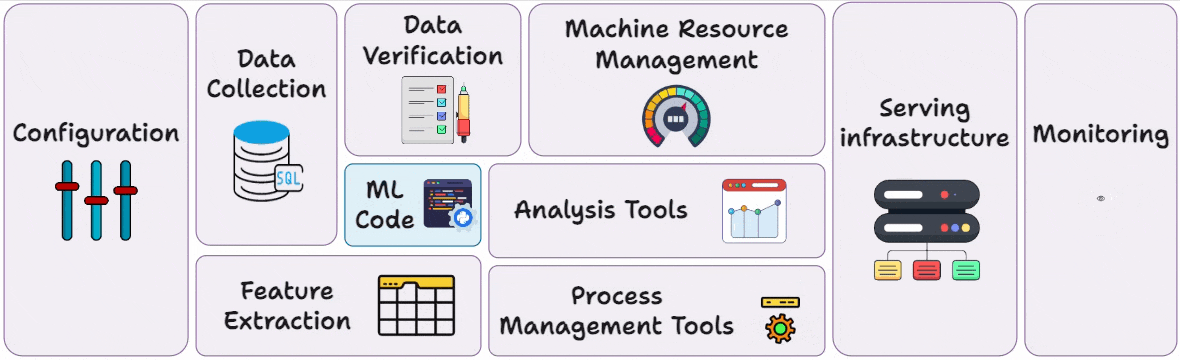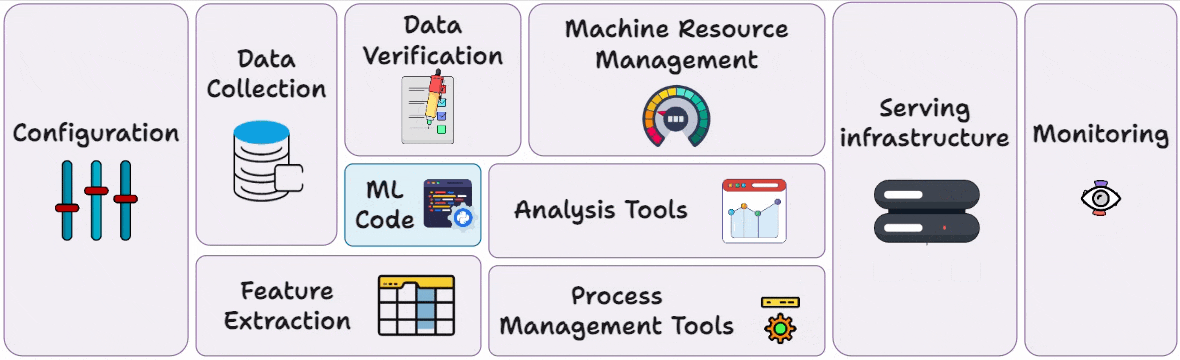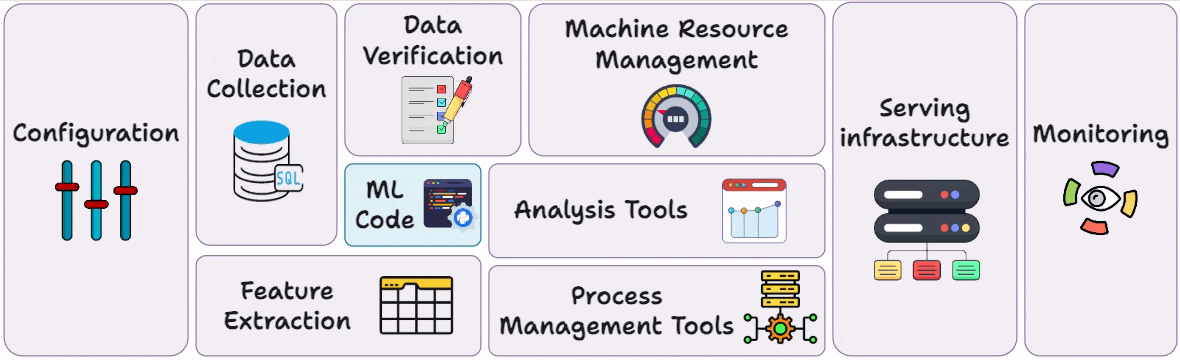
MLOps seeks to manage this complexity by applying reliable software engineering and DevOps practices to ML systems, ensuring that all these components work in concert to deliver value.
This MLOps and LLMOps crash course will provide you with a thorough explanation and systems-level thinking to build AI models for production settings.
Just as the MCP crash course, each chapter will clearly explain necessary concepts, provide examples, diagrams, and implementations.